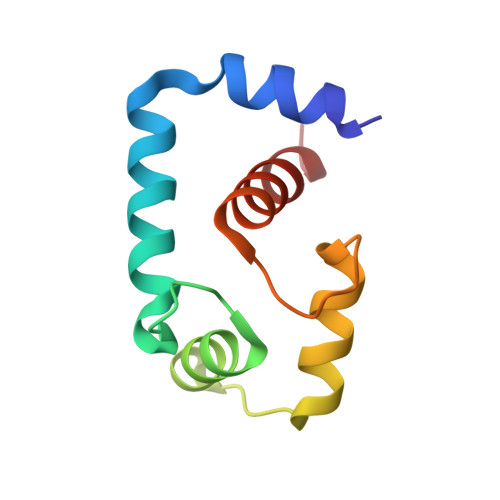
Structure and Dynamics of the Acidosis-Resistant A162H Mutant of the Switch Region of Troponin I Bound to the Regulatory Domain of Troponin C.
Pineda-Sanabria, S.E., Robertson, I.M., Sykes, B.D.(2015) Biochemistry 54: 3583-3593
- PubMed: 25996354
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.5b00178
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2MZP - PubMed Abstract:
Intracellular acidosis lowers the Ca²⁺ sensitivity of cardiac muscle, which results in decreased force generation, decreased cardiac output, and, eventually, heart failure. The A162H mutant of cardiac troponin I in the thin filament turns the heart acidosis-resistant. Physiological and structural studies have provided insights into the mechanism of protection by the A162H substitution; however, the effect of other native residues of cardiac troponin I is not fully understood. In this study, we determined the structure of the A162H mutant of the switch region of cardiac troponin I bound to the regulatory domain of troponin C at pH 6.1, and the dynamics as a function of pH, by NMR spectroscopy to evaluate the changes induced by protonation of A162H. The results indicate that A162H induces a transitory curved conformation on troponin I that promotes contraction, but it is countered by residue E164 to ensure proper relaxation. Our model explains the absence of diastolic impairment in the gain-of-function phenotype induced by the A162H substitution as well as the effects of a variety of mutants studied previously. The description of this mechanism underlines the fine quality of regulation on cardiac muscle contraction and anticipates pharmacological agents that induce modest changes in the contraction-relaxation equilibrium to produce marked effects in cardiac performance.