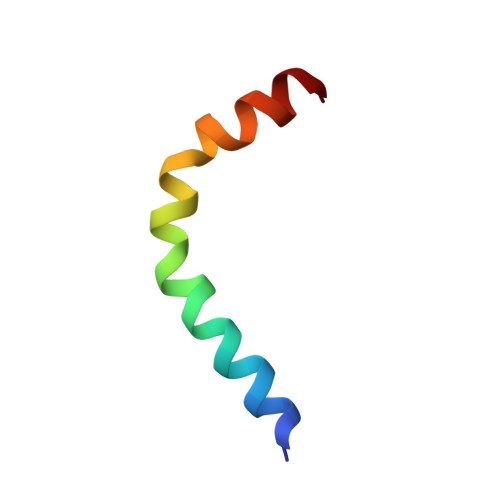
Aedesin: structure and antimicrobial activity against multidrug resistant bacterial strains.
Godreuil, S., Leban, N., Padilla, A., Hamel, R., Luplertlop, N., Chauffour, A., Vittecoq, M., Hoh, F., Thomas, F., Sougakoff, W., Lionne, C., Yssel, H., Misse, D.(2014) PLoS One 9: e105441-e105441
- PubMed: 25162372
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0105441
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2MMM - PubMed Abstract:
Multidrug resistance, which is acquired by both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, causes infections that are associated with significant morbidity and mortality in many clinical settings around the world. Because of the rapidly increasing incidence of pathogens that have become resistant to all or nearly all available antibiotics, there is a need for a new generation of antimicrobials with a broad therapeutic range for specific applications against infections. Aedesin is a cecropin-like anti-microbial peptide that was recently isolated from dengue virus-infected salivary glands of the Aedes aegypti mosquito. In the present study, we have refined the analysis of its structural characteristics and have determined its antimicrobial effects against a large panel of multidrug resistant bacterial strains, directly isolated from infected patients. Based the results from nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy analysis, Aedesin has a helix-bend-helix structure typical for a member of the family of α-helix anti-microbial peptides. Aedesin efficiently killed Gram-negative bacterial strains that display the most worrisome resistance mechanisms encountered in the clinic, including resistance to carbapenems, aminoglycosides, cephalosporins, 4th generation fluoroquinolones, folate inhibitors and monobactams. In contrast, Gram-positive strains were insensitive to the lytic effects of the peptide. The anti-bacterial activity of Aedesin was found to be salt-resistant, indicating that it is active under physiological conditions encountered in body fluids characterized by ionic salt concentrations. In conclusion, because of its strong lytic activity against multidrug resistant Gram-negative bacterial strains displaying all types of clinically relevant resistance mechanisms known today, Aedesin might be an interesting candidate for the development of alternative treatment for infections caused by these types of bacteria.
- Centre Hospitalier Régional Universitaire de Montpellier, Hôpital Arnaud de Villeneuve, Département de Bactériologie-Virologie, Montpellier, France.
Organizational Affiliation: