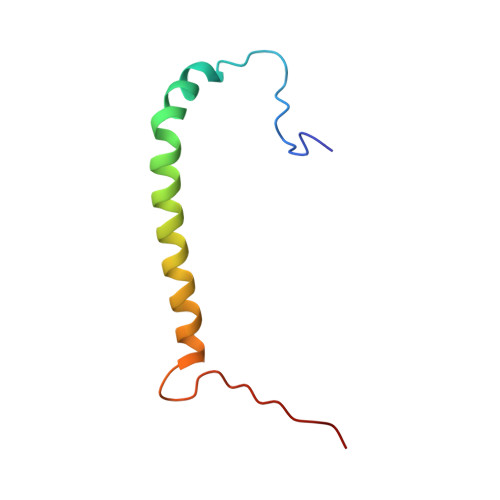
Structure of the Na,K-ATPase regulatory protein FXYD2b in micelles: Implications for membrane-water interfacial arginines.
Gong, X.M., Ding, Y., Yu, J., Yao, Y., Marassi, F.M.(2015) Biochim Biophys Acta 1848: 299-306
- PubMed: 24794573
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2014.04.021
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2MKV - PubMed Abstract:
FXYD2 is a membrane protein responsible for regulating the function of the Na,K-ATPase in mammalian kidney epithelial cells. Here we report the structure of FXYD2b, one of two splice variants of the protein, determined by NMR spectroscopy in detergent micelles. Solid-state NMR characterization of the protein embedded in phospholipid bilayers indicates that several arginine side chains may be involved in hydrogen bond interactions with the phospholipid polar head groups. The structure and the NMR data suggest that FXYD2b could regulate the Na,K-ATPase by modulating the effective membrane surface electrostatics near the ion binding sites of the pump.
- Sanford-Burnham Medical Research Institute, 10901 North Torrey Pines Road, La Jolla, CA 92037, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: