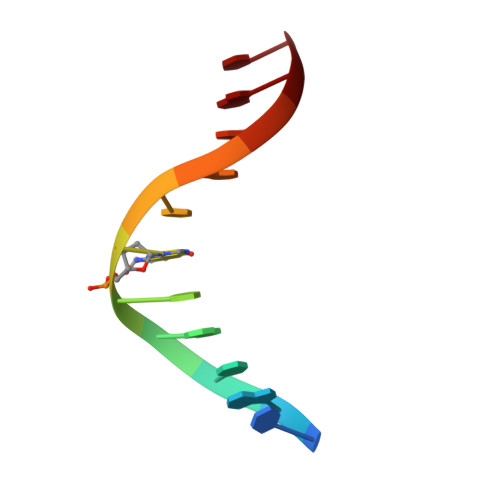
NMR structure of duplex DNA containing the alpha-OH-PdG.dA base pair: a mutagenic intermediate of acrolein.
Zaliznyak, T., Lukin, M., El-khateeb, M., Bonala, R., Johnson, F., de los Santos, C.(2010) Biopolymers 93: 391-401
- PubMed: 20049919
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/bip.21366
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2LSZ, 2LT0 - PubMed Abstract:
Acrolein, a cell metabolic product and main component of cigarette smoke, reacts with DNA generating alpha-OH-PdG lesions, which have the ability to pair with dATP during replication thereby causing G to T transversions. We describe the solution structure of an 11-mer DNA duplex containing the mutagenic alpha-OH-PdG.dA base pair intermediate, as determined by solution nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy and retrained molecular dynamics (MD) simulations. The NMR data support a mostly regular right-handed helix that is only perturbed at its center by the presence of the lesion. Undamaged residues of the duplex are in anti orientation, forming standard Watson-Crick base pairs alignments. Duplication of proton signals at and near the damaged base pair reveals the presence of two enantiomeric duplexes, thus establishing the exocyclic nature of the lesion. The alpha-OH-PdG adduct assumes a syn conformation pairing to its partner dA base that is protonated at pH 6.6. The three-dimensional structure obtained by restrained molecular dynamics simulations show hydrogen bond interactions that stabilize alpha-OH-PdG in a syn conformation and across the lesion containing base pair. We discuss the implications of the structures for the mutagenic bypass of acrolein lesions.
- Department of Pharmacological Sciences, Stony Brook University, School of Medicine Stony Brook, NY 11794-8651, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: