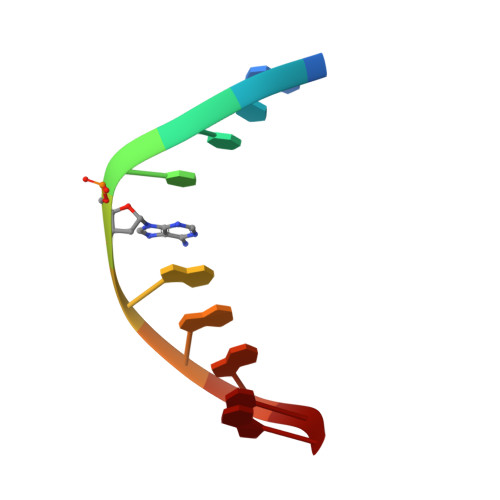
DNA sequence context conceals alpha-anomeric lesions.
Johnson, C.N., Spring, A.M., Desai, S., Cunningham, R.P., Germann, M.W.(2012) J Mol Biology 416: 425-437
- PubMed: 22227386
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2011.12.051
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2LIB - PubMed Abstract:
DNA sequence context has long been known to modulate detection and repair of DNA damage. Recent studies using experimental and computational approaches have sought to provide a basis for this observation. We have previously shown that an α-anomeric adenosine (αA) flanked by cytosines (5'CαAC-3') resulted in a kinked DNA duplex with an enlarged minor groove. Comparison of different flanking sequences revealed that a DNA duplex containing a 5'CαAG-3' motif exhibits unique substrate properties. However, this substrate was not distinguished by unusual thermodynamic properties. To understand the structural basis of the altered recognition, we have determined the solution structure of a DNA duplex with a 5'CαAG-3' core, using an extensive set of restraints including dipolar couplings and backbone torsion angles. The NMR structure exhibits an excellent agreement with the data (total R(X) <5.3%). The αA base is intrahelical, in a reverse Watson-Crick orientation, and forms a weak base pair with a thymine of the opposite strand. In comparison to the DNA duplex with a 5'CαAC-3' core, we observe a significant reduction of the local perturbation (backbone, stacking, tilt, roll, and twist), resulting in a straighter DNA with narrower minor groove. Overall, these features result in a less perturbed DNA helix and obscure the presence of the lesion compared to the 5'CαAC-3' sequence. The improved stacking of the 5'CαAG-3' core also affects the energetics of the DNA deformation that is required to form a catalytically competent complex. These traits provide a rationale for the modulation of the recognition by endonuclease IV.
- Department of Chemistry, Georgia State University, Atlanta, GA 30303, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: