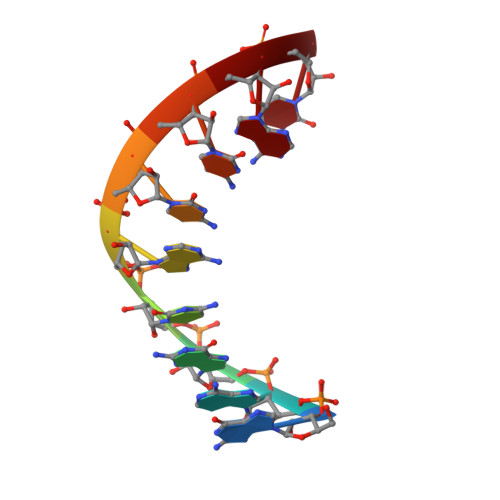
Structural basis of the RNase H1 activity on stereo regular borano phosphonate DNA/RNA hybrids.
Johnson, C.N., Spring, A.M., Sergueev, D., Shaw, B.R., Germann, M.W.(2011) Biochemistry 50: 3903-3912
- PubMed: 21443203
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi200083d
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2LAR, 2LB4 - PubMed Abstract:
Numerous DNA chemistries for improving oligodeoxynucleotide (ODN)-based RNA targeting have been explored. The majority of the modifications render the ODN/RNA target insensitive to RNase H1. Borano phosphonate ODN's are among the few modifications that are tolerated by RNase H1. To understand the effect of the stereochemistry of the BH(3) modification on the nucleic acid structure and RNase H1 enzyme activity, we have investigated two DNA/RNA hybrids containing either a R(P) or S(P) BH(3) modification by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy. T(M) studies show that the stabilities of R(P) and S(P) modified DNA/RNA hybrids are essentially identical (313.8 K) and similar to that of an unmodified control (312.9 K). The similarity is also reflected in the imino proton spectra. To characterize such similar structures, we used a large number of NMR restraints (including dipolar couplings and backbone torsion angles) to determine structural features that were important for RNase H1 activity. The final NMR structures exhibit excellent agreement with the data (total R(x) values of <6%) with helical properties between those of an A and B helix. Subtle backbone variations are observed in the DNA near the modification, while the RNA strands are relatively unperturbed. In the case of the S(P) modification, for which more perturbations are recorded, a slightly narrower minor groove is also obtained. Unique NOE base contacts localize the S(P) BH(3) group in the major groove while the R(P) BH(3) group points away from the DNA. However, this creates a potential clash of the R(P) BH(3) groups with important RNase H1 residues in a complex, while the S(P) BH(3) groups could be tolerated. We therefore predict that on the basis of our NMR structures a fully R(P) BH(3) DNA/RNA hybrid would not be a substrate for RNase H1.
- Department of Chemistry, Georgia State University, Atlanta, Georgia 30302-3965, United States.
Organizational Affiliation: