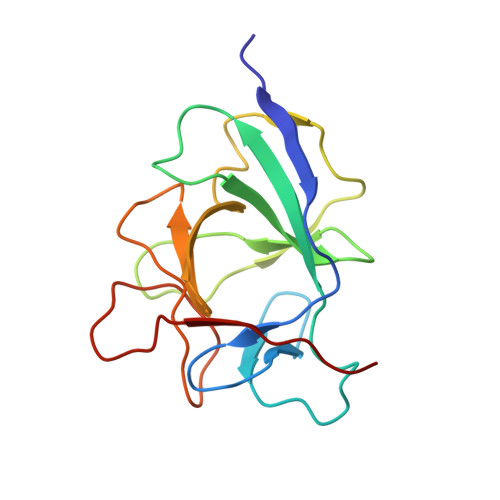
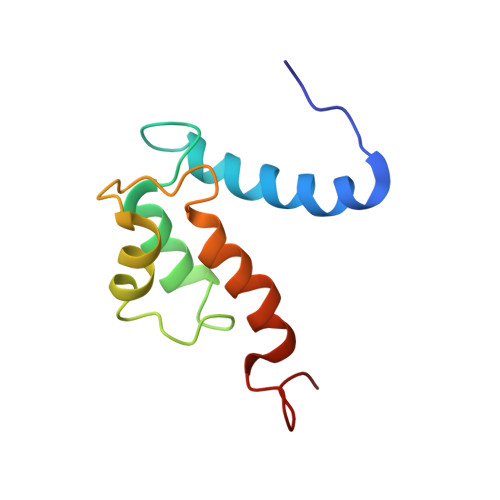
The IL1alpha-S100A13 heterotetrameric complex structure: a component in the non-classical pathway for interleukin 1alpha secretion
Mohan, S.K., Yu, C.(2011) J Biological Chem 286: 14608-14617
- PubMed: 21270123
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.201954
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2L5X - PubMed Abstract:
Interleukin 1α (IL1α) plays an important role in several key biological functions, such as angiogenesis, cell proliferation, and tumor growth in several types of cancer. IL1α is a potent cytokine that induces a wide spectrum of immunological and inflammatory activities. The biological effects of IL1α are mediated through the activation of transmembrane receptors (IL1Rs) and therefore require the release of the protein into the extracellular space. IL1α is exported through a non-classical release pathway involving the formation of a specific multiprotein complex, which includes IL1α and S100A13. Because IL1α plays an important role in cell proliferation and angiogenesis, inhibiting the formation of the IL1α-S100A13 complex would be an effective strategy to inhibit a wide range of cancers. To understand the molecular events in the IL1α release pathway, we studied the structure of the IL1α-S100A13 tetrameric complex, which is the key complex formed during the non-classical pathway of IL1α release.
- Department of Chemistry, National Tsing Hua University, Hsinchu 30013, Taiwan.
Organizational Affiliation: