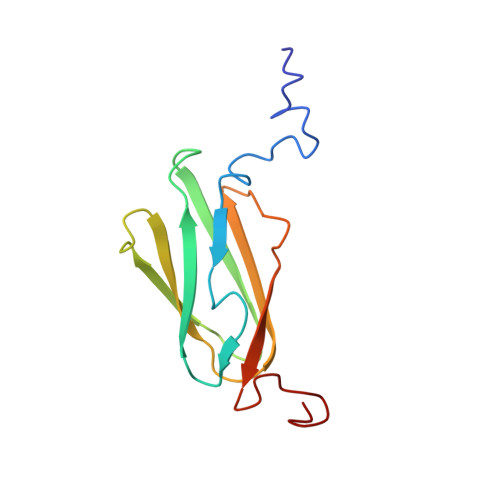
Migfilin, a molecular switch in regulation of integrin activation.
Ithychanda, S.S., Das, M., Ma, Y.Q., Ding, K., Wang, X., Gupta, S., Wu, C., Plow, E.F., Qin, J.(2009) J Biological Chem 284: 4713-4722
- PubMed: 19074766
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M807719200
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2K9U - PubMed Abstract:
The linkage of heterodimeric (alpha/beta) integrin receptors with their extracellular matrix ligands and intracellular actin cytoskeleton is a fundamental step for controlling cell adhesion and migration. Binding of the actin-linking protein, talin, to integrin beta cytoplasmic tails (CTs) induces high affinity ligand binding (integrin activation), whereas binding of another actin-linking protein, filamin, to the integrin beta CTs negatively regulates this process by blocking the talin-integrin interaction. Here we show structurally that migfilin, a novel cytoskeletal adaptor highly enriched in the integrin adhesion sites, strongly interacts with the same region in filamin where integrin beta CTs bind. We further demonstrate that the migfilin interaction dissociates filamin from integrin and promotes the talin/integrin binding and integrin activation. Migfilin thus acts as a molecular switch to disconnect filamin from integrin for regulating integrin activation and dynamics of extracellular matrix-actin linkage.
- Department of Molecular Cardiology, Lerner Research Institute, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, Ohio 44195, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: