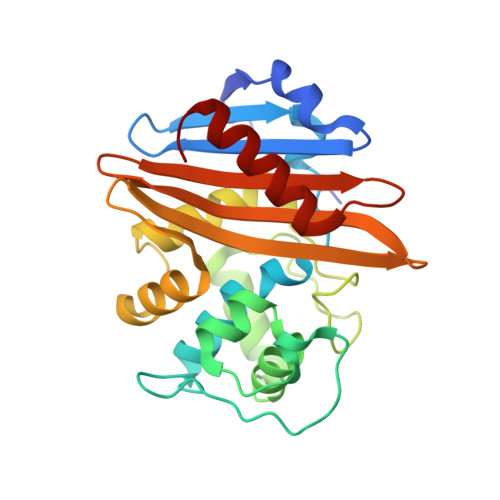
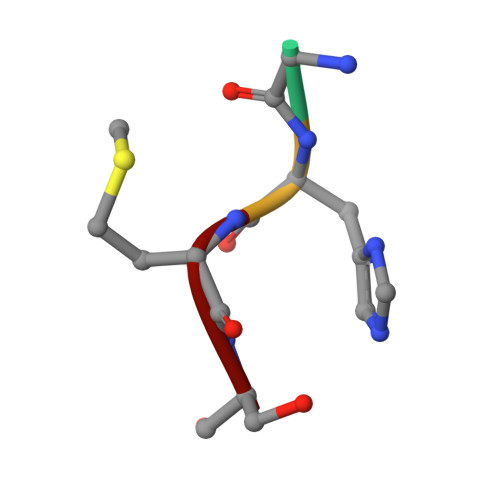
Unbound and Acylated Structures of the Mecr1 Extracellular Antibiotic-Sensor Domain Provide Insights Into the Signal-Transduction System that Triggers Methicillin Resistance.
Marrero, A., Mallorqui-Fernandez, G., Guevara, T., Garcia-Castellanos, R., Gomis-Ruth, F.X.(2006) J Mol Biology 361: 506
- PubMed: 16846613
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2006.06.046
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2IWB, 2IWC, 2IWD - PubMed Abstract:
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) strains are responsible for most hospital-onset bacterial infections. Lately, they have become a major threat to the community through infections of skin, soft tissue and respiratory tract, and subsequent septicaemia or septic shock. MRSA strains are resistant to most beta-lactam antibiotics (BLAs) as a result of the biosynthesis of a penicillin-binding protein with low affinity for BLAs, called PBP2a, PBP2' or MecA. This response is regulated by the chromosomal mec-divergon, which encodes a signal-transduction system including a transcriptional repressor, MecI, and a sensor/transducer, MecR1, as well as the structural mecA gene. This system is similar to those encoded by bla divergons in S. aureus and Bacillus licheniformis. MecR1 comprises an integral-membrane latent metalloprotease domain facing the cytosol and an extracellular sensor domain. The latter binds BLAs and transmits a signal through the membrane that eventually triggers activation of the metalloprotease moiety, which in turn switches off MecI-induced repression of mecA transcription. The MecR1 sensor domain, MecR1-PBD, reveals a two-domain structure of alpha/beta-type fold reminiscent of penicillin-binding proteins and beta-lactamases, and a catalytic serine residue as the ultimate cause for BLA-binding. Covalent complexes with benzylpenicillin and oxacillin provide evidence that serine acylation does not entail significant structural changes, thus supporting the hypothesis that additional extracellular segments of MecR1 are involved in signal transmission. The chemical nature of the residues shaping the active-site cleft favours stabilisation of the acyl enzyme complexes in MecR1-PBD, in contrast to the closely related OXA beta-lactamases, where the cleft is more likely to promote subsequent hydrolysis. The present structural data provide insights into the mec-encoded BLA-response mechanism and an explanation for kinetic differences in signal transmission with the related bla-encoded systems.
- Institut de Biologia Molecular de Barcelona, C.I.D.-C.S.I.C. C/Jordi Girona, 18-26 08034 Barcelona, Spain.
Organizational Affiliation: