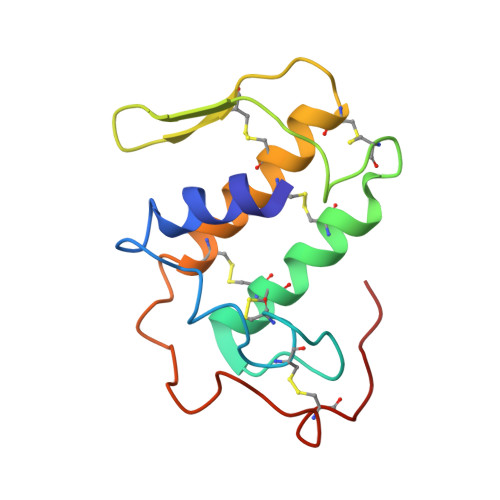
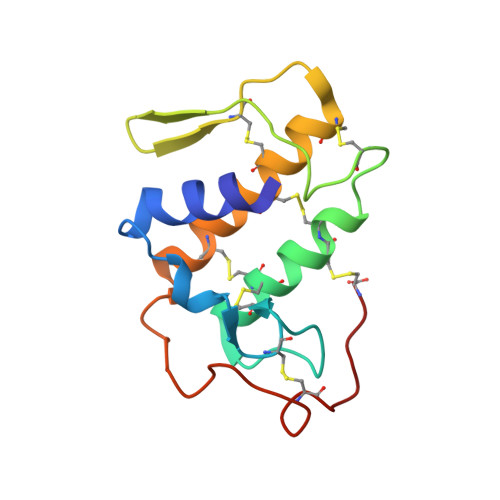
Structural and pharmacological comparison of daboiatoxin from Daboia russelli siamensis with viperotoxin F and vipoxin from other vipers.
Gopalan, G., Thwin, M.M., Gopalakrishnakone, P., Swaminathan, K.(2007) Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 63: 722-729
- PubMed: 17505111
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S0907444907016204
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2H4C - PubMed Abstract:
Russell's viper (Vipera russelli, also known as Daboia russelli) is one of the major causes of fatal snakebites. To date, five Daboia russelli subspecies have been recognized. Daboiatoxin (DbTx) is the main lethal phospholipase A(2) (PLA(2)) toxin in the venom of D. russelli siamensis (Myanmar viper) and has strong neurotoxic, myotoxic and cytotoxic activities. DbTx and its homologous neurotoxins viperotoxin F from D. russelli formosensis (Taiwan viper) and vipoxin from the Bulgarian sand viper V. ammodytes meridionalis consist of complexes between a nontoxic acidic PLA(2) protein and an enzymatically active basic PLA(2). DbTx and viperotoxin F are presynaptic toxins, while vipoxin is postsynaptic. The two chains of DbTx have been separated and their PLA(2) enzymatic activity has been measured using the secretory PLA(2) assay kit. The enzymatic activity of DbTx chain B is reduced by 30% of its original activity by chain A in a unimolar ratio, thus indicating that DbTx chain A acts as an inhibitor. The lethal activity of the two chains has also been studied in male albino mice and chain A is less lethal than chain B. The crystal structure of DbTx has also been determined and its structural details are compared with those of the two homologues. Furthermore, an attempt is made to correlate the sequence and structural determinants of these toxins with their enzymatic activities and their pharmacological effects.
- Department of Biological Sciences, National University of Singapore, Singapore 117543, Singapore.
Organizational Affiliation: