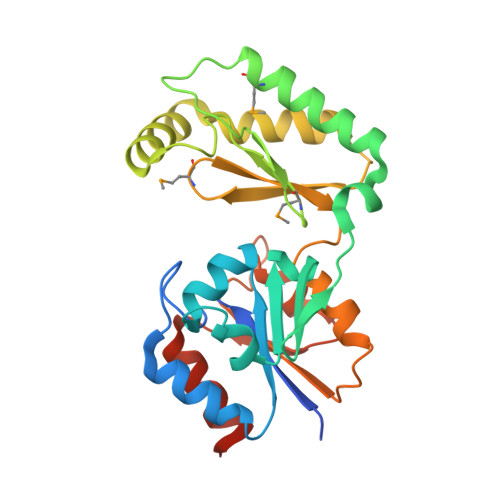
The X-ray crystal structures of human alpha-phosphomannomutase 1 reveal the structural basis of congenital disorder of glycosylation type 1a.
Silvaggi, N.R., Zhang, C., Lu, Z., Dai, J., Dunaway-Mariano, D., Allen, K.N.(2006) J Biological Chem 281: 14918-14926
- PubMed: 16540464
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M601505200
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2FUC, 2FUE - PubMed Abstract:
Congenital disorder of glycosylation type 1a (CDG-1a) is a congenital disease characterized by severe defects in nervous system development. It is caused by mutations in alpha-phosphomannomutase (of which there are two isozymes, alpha-PMM1 and alpha-PPM2). Here we report the x-ray crystal structures of human alpha-PMM1 in the open conformation, with and without the bound substrate, alpha-D-mannose 1-phosphate. Alpha-PMM1, like most haloalkanoic acid dehalogenase superfamily (HADSF) members, consists of two domains, the cap and core, which open to bind substrate and then close to provide a solvent-exclusive environment for catalysis. The substrate phosphate group is observed at a positively charged site of the cap domain, rather than at the core domain phosphoryl-transfer site defined by the Asp(19) nucleophile and Mg(2+) cofactor. This suggests that substrate binds first to the cap and then is swept into the active site upon cap closure. The orientation of the acid/base residue Asp(21) suggests that alpha-phosphomannomutase (alpha-PMM) uses a different method of protecting the aspartylphosphate from hydrolysis than the HADSF member beta-phosphoglucomutase. It is hypothesized that the electrostatic repulsion of positive charges at the interface of the cap and core domains stabilizes alpha-PMM1 in the open conformation and that the negatively charged substrate binds to the cap, thereby facilitating its closure over the core domain. The two isozymes, alpha-PMM1 and alpha-PMM2, are shown to have a conserved active-site structure and to display similar kinetic properties. Analysis of the known mutation sites in the context of the structures reveals the genotype-phenotype relationship underlying CDG-1a.
- Department of Physiology and Biophysics, Boston University School of Medicine, 715 Albany Street, Boston, MA 02118, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: