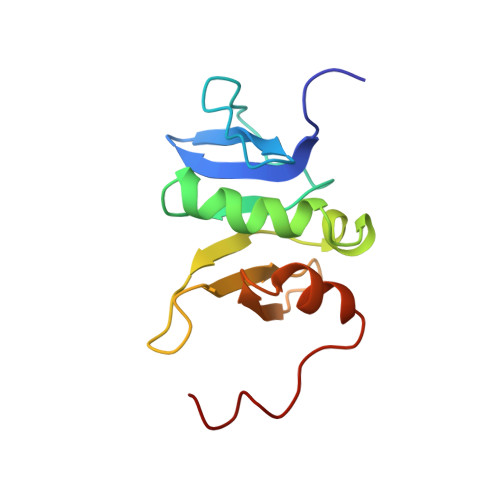
Domain architecture and structure of the bacterial cell division protein DivIB
Robson, S.A., King, G.F.(2006) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103: 6700-6705
- PubMed: 16618922
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0601397103
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1YR1, 2ALJ - PubMed Abstract:
Bacterial cytokinesis requires the coordinated assembly of a complex of proteins, collectively known as the divisome, at the incipient division site. DivIB/FtsQ is a conserved component of the divisome in bacteria with cell walls, suggesting that it plays a role in synthesis and/or remodeling of septal peptidoglycan. We demonstrate that the extracytoplasmic region of DivIB comprises three discrete domains that we designate alpha, beta, and gamma from the N to C terminus. The alpha-domain is proximal to the cytoplasmic membrane and coincident with the polypeptide transport-associated domain that was proposed previously to function as a molecular chaperone. The beta-domain has a unique 3D fold, with no eukaryotic counterpart, and we show that it interconverts between two discrete conformations via cis-trans isomerization of a Tyr-Pro peptide bond. We propose that this isomerization might modulate protein-protein interactions of the flanking alpha- and gamma-domains. The C-terminal gamma-domain is unstructured in the absence of other divisomal proteins, but we show that it is critical for DivIB function.
- Department of Molecular, Microbial, and Structural Biology and Partnership for Excellence in Structural Biology, University of Connecticut Health Center, 263 Farmington Avenue, Farmington, CT 06030-3305, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: