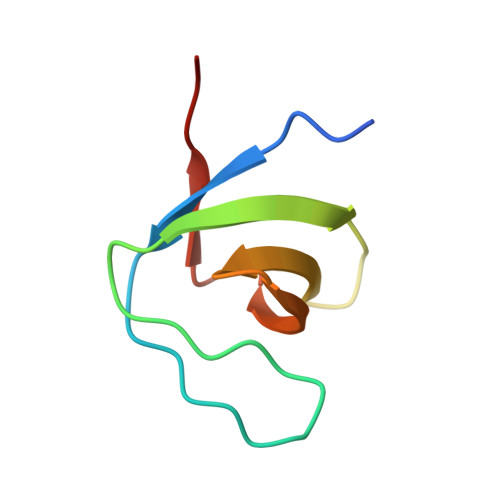
Cbl promotes clustering of endocytic adaptor proteins.
Jozic, D., Cardenes, N., Deribe, Y.L., Moncalian, G., Hoeller, D., Groemping, Y., Dikic, I., Rittinger, K., Bravo, J.(2005) Nat Struct Mol Biol 12: 972-979
- PubMed: 16228008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb1000
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2AK5, 2BZ8 - PubMed Abstract:
The ubiquitin ligases c-Cbl and Cbl-b play a crucial role in receptor downregulation by mediating multiple monoubiquitination of receptors and promoting their sorting for lysosomal degradation. Their function is modulated through interactions with regulatory proteins including CIN85 and PIX, which recognize a proline-arginine motif in Cbl and thus promote or inhibit receptor endocytosis. We report the structures of SH3 domains of CIN85 and beta-PIX in complex with a proline-arginine peptide from Cbl-b. Both structures reveal a heterotrimeric complex containing two SH3 domains held together by a single peptide. Trimerization also occurs in solution and is facilitated by the pseudo-symmetrical peptide sequence. Moreover, ternary complexes of CIN85 and Cbl are formed in vivo and are important for the ability of Cbl to promote epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) downregulation. These results provide molecular explanations for a novel mechanism by which Cbl controls receptor downregulation.
- Division of Protein Structure, National Institute for Medical Research, The Ridgeway, London NW7 1AA, UK.
Organizational Affiliation: