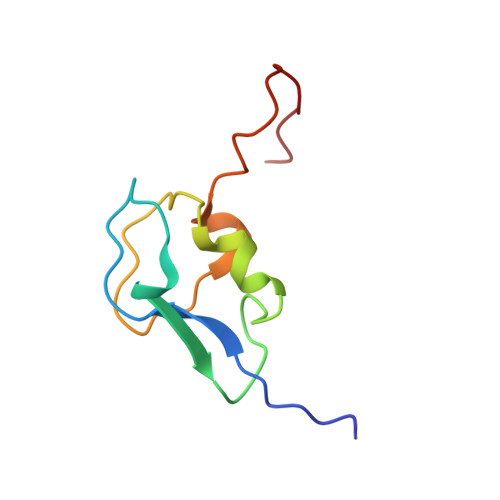
Solution structure of the antifreeze-like domain of human sialic acid synthase
Hamada, T., Ito, Y., Abe, T., Hayashi, F., Guntert, P., Inoue, M., Kigawa, T., Terada, T., Shirouzu, M., Yoshida, M., Tanaka, A., Sugano, S., Yokoyama, S., Hirota, H.(2006) Protein Sci 15: 1010-1016
- PubMed: 16597820
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1110/ps.051700406
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1WVO - PubMed Abstract:
The structure of the C-terminal antifreeze-like (AFL) domain of human sialic acid synthase was determined by NMR spectroscopy. The structure comprises one alpha- and two single-turn 3(10)-helices and two beta-strands, and is similar to those of the type III antifreeze proteins. Evolutionary trace analyses of the type III antifreeze protein family suggested that the class-specific residues in the human and bacterial AFL domains are important for their substrate binding, while the class-specific residues of the fish antifreeze proteins are gathered on the ice-binding surface.
- RIKEN Genomic Sciences Center, Yokohama 230-0045, Japan.
Organizational Affiliation: