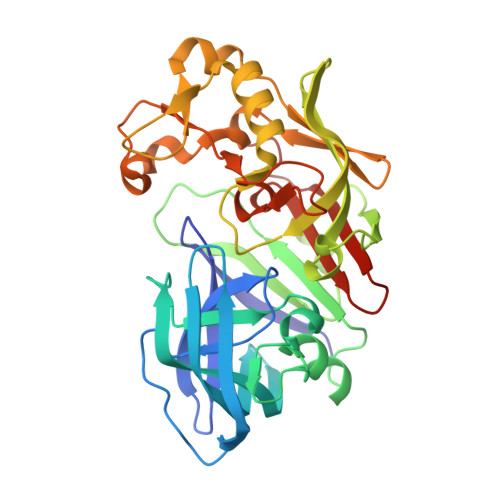
Crystal Structure of Aspartic Proteinase from Irpex lacteus in Complex with Inhibitor Pepstatin
Fujimoto, Z., Fujii, Y., Kaneko, S., Kobayashi, H., Mizuno, H.(2004) J Mol Biology 341: 1227-1235
- PubMed: 15321718
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2004.06.049
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1WKR - PubMed Abstract:
The crystal structure of Irpex lacteus aspartic proteinase (ILAP) in complex with pepstatin (a six amino acid residue peptide-like inhibitor) was determined at 1.3A resolution. ILAP is a pepsin-like enzyme, widely distributed in nature, with high milk-clotting activity relative to proteolytic activity. The overall structure was in good topological agreement with pepsin and other aspartic proteases. The structure and interaction pattern around the catalytic site were conserved, in agreement with the other aspartic proteinase/inhibitor complex structures reported previously. The high-resolution data also supported the transition state model, as proposed previously for the catalytic mechanism of aspartic proteinase. Unlike the other aspartic proteinases, ILAP was found to require hydrophobic residues either in the P(1) or P(1') site, and also in the P(4) and/or P(3) site(s) for secondary interactions. The inhibitor complex structure also revealed the substrate binding mechanism of ILAP at the P(3) and P(4) site of the substrate, where the inserted loop built up the unique hydrophobic pocket at the P(4) site.
- Department of Biochemistry, National Institute of Agrobiological Sciences, Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-8602, Japan. zui@affrc.go.jp
Organizational Affiliation: