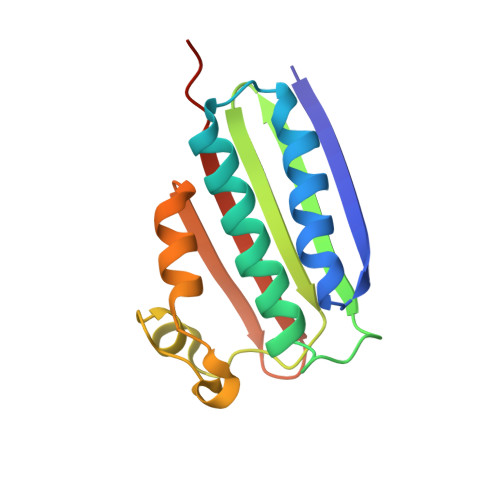
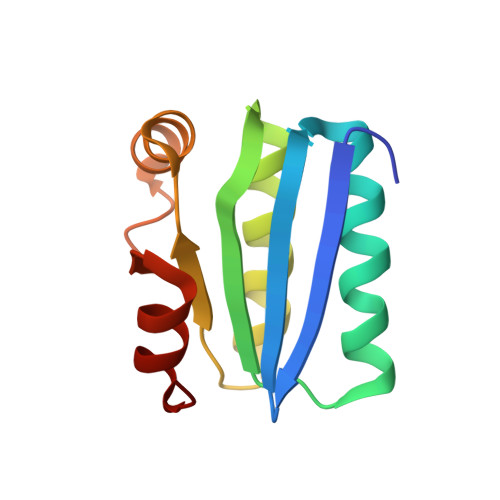
Crystal Structures of the ADP and ATP Bound Forms of the Bacillus Anti-sigma Factor SpoIIAB in Complex with the Anti-anti-sigma SpoIIAA.
Masuda, S., Murakami, K.S., Wang, S., Olson, C.A., Donigian, J., Leon, F., Darst, S.A., Campbell, E.A.(2004) J Mol Biology 340: 941-956
- PubMed: 15236958
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2004.05.040
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1TH8, 1THN, 1TID, 1TIL - PubMed Abstract:
Cell type-specific transcription during Bacillus sporulation is established by sigma(F), the activity of which is controlled by a regulatory circuit involving the anti-sigma factor and serine kinase SpoIIAB, and the anti-anti-sigma SpoIIAA. When ATP is present in the nucleotide-binding site of SpoIIAB, SpoIIAA is phosphorylated, followed by dissociation. The nucleotide-binding site of SpoIIAB is left bound to ADP. SpoIIAB(ADP) can bind an unphosphorylated molecule of SpoIIAA as a stable binding partner. Thus, in this circuit, SpoIIAA plays a dual role as a substrate of the SpoIIAB kinase activity, as well as a tight binding inhibitor. Crystal structures of both the pre-phosphorylation complex and the inhibitory complex, SpoIIAB(ATP) and SpoIIAB(ADP) bound to SpoIIAA, respectively, have been determined. The structural differences between the two forms are subtle and confined to interactions with the phosphoryl groups of the nucleotides. The structures reveal details of the SpoIIAA:SpoIIAB interactions and how phosphorylated SpoIIAA dissociates from SpoIIAB(ADP). Finally, the results confirm and expand upon the docking model for SpoIIAA function as an anti-anti-sigma in releasing sigma(F) from SpoIIAB.
- The Rockefeller University, 1230 York Avenue, New York, NY 10021, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: