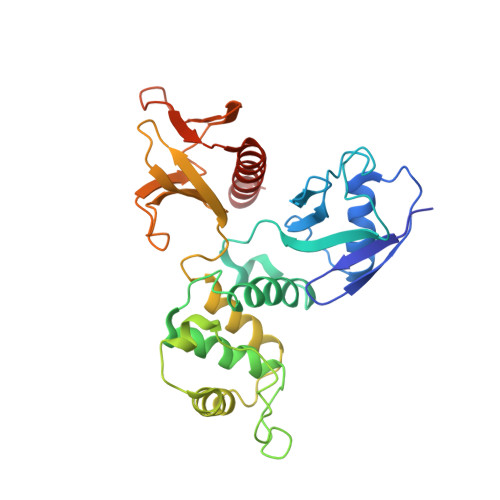
The EBP50-moesin interaction involves a binding site regulated by direct masking on the FERM domain
Finnerty, C.M., Chambers, D., Ingraffea, J., Faber, H.R., Karplus, P.A., Bretscher, A.(2004) J Cell Sci 117: 1547-1552
- PubMed: 15020681
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.01038
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1SGH - PubMed Abstract:
Members of the ezrin-radixin-moesin (ERM) protein family serve as regulated microfilament-membrane crosslinking proteins that, upon activation, bind the scaffolding protein ERM-phosphoprotein of 50 kDa (EBP50). Here we report a 3.5 A resolution diffraction analysis of a complex between the active moesin N-terminal FERM domain and a 38 residue peptide from the C terminus of EBP50. This crystallographic result, combined with sequence and structural comparisons, suggests that the C-terminal 11 residues of EBP50 binds as an alpha-helix at the same site occupied in the dormant monomer by the last 11 residues of the inhibitory moesin C-terminal tail. Biochemical support for this interpretation derives from in vitro studies showing that appropriate mutations in both the EBP50 tail peptide and the FERM domain reduce binding, and that a peptide representing just the C-terminal 14 residues of EBP50 also binds to moesin. Combined with the recent identification of the I-CAM-2 binding site on the ERM FERM domain (Hamada, K., Shimizu, T., Yonemura, S., Tsukita, S., and Hakoshima, T. (2003) EMBO J. 22, 502-514), this study reveals that the FERM domain contains two distinct binding sites for membrane-associated proteins. The contribution of each ligand to ERM function can now be dissected by making structure-based mutations that specifically affect the binding of each ligand.
- Department of Molecular Biology and Genetics, Biotechnology Building, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY 14853, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: