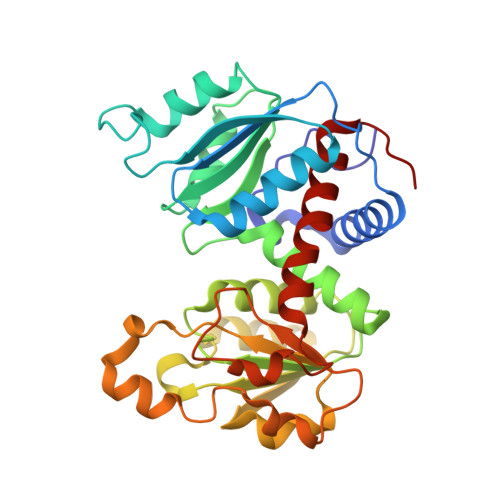
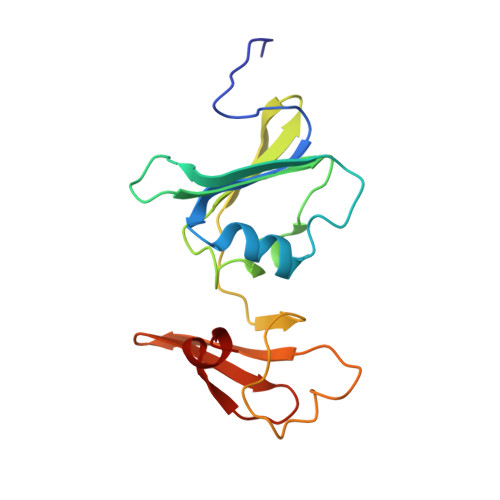
Products in the T-State of Aspartate Transcarbamylase: Crystal Structure of the Phosphate and N-Carbamyl-l-aspartate Ligated Enzyme
Huang, J., Lipscomb, W.N.(2004) Biochemistry 43: 6422-6426
- PubMed: 15157076
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi0302144
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1R0C - PubMed Abstract:
The structure of aspartate transcarbamylase of Escherichia coli ligated to products (phosphate and N-carbamyl-l-aspartate) has been determined at 2.37 A resolution (R-factor = 0.23, R(free) = 0.27). Results might indicate a product release mode, rather than close analogues to the transition state like those found in our earlier studies of other ligands (N-phosphonacetyl-L-aspartate, carbamyl phosphate plus malonate, phosphonoacetamide plus malonate, or citrate plus phosphate). Ordered product release, first carbamylaspartate (CLA) and then phosphate, might be facilitated by a 4 A movement of phosphate from the substrate-analogue position to the product (phosphate) binding position, and by a somewhat similar release movement of the other product (CLA) relative to its analogue (citrate). This movement is consistent with earlier studies of binding of either pyrophosphate or phosphate alone [Honzatko, R. B., and Lipscomb, W. N. (1982) J. Mol. Biol. 160, 265-286].
- Department of Chemistry and Chemical Biology, Harvard University, Cambridge, Massachusetts 02138, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: