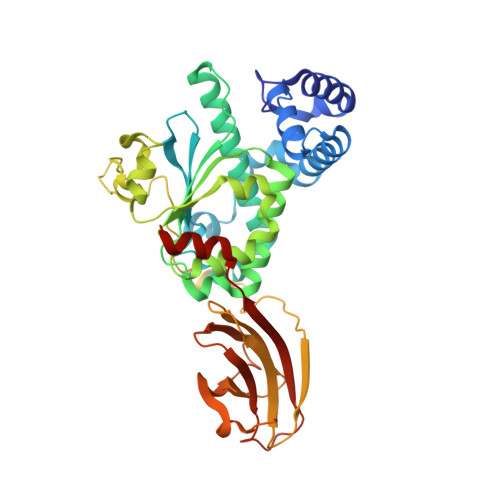
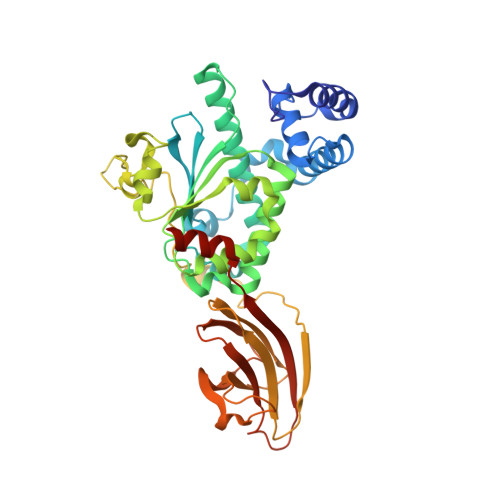
Supernatant Protein Factor in Complex with Rrr-Alpha-Tocopherylquinone: A Link between Oxidized Vitamin E and Cholesterol Biosynthesis
Stocker, A., Baumann, U.(2003) J Mol Biology 332: 759
- PubMed: 12972248
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-2836(03)00924-0
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1OLM - PubMed Abstract:
The vast majority of monomeric lipid transport in nature is performed by lipid-specific protein carriers. This class of proteins can enclose cognate lipid molecules in a hydrophobic cavity and transport them across the aqueous environment. Supernatant protein factor (SPF) is an enigmatic representative of monomeric lipid transporters belonging to the SEC14 family. SPF stimulates squalene epoxidation, a downstream step of the cholesterol biosynthetic pathway, by an unknown mechanism. Here, we present the three-dimensional crystal structure of human SPF in complex with RRR-alpha-tocopherylquinone, the major physiological oxidation product of RRR-alpha-tocopherol, at a resolution of 1.95A. The structure of the complex reveals how SPF sequesters RRR-alpha-tocopherylquinone (RRR-alpha-TQ) in its protein body and permits a comparison with the recently solved structure of human alpha-tocopherol transfer protein (alpha-TTP) in complex with RRR-alpha-tocopherol. Recent findings have shown that RRR-alpha-TQ is reduced in vivo to RRR-alpha-TQH(2), the latter has been suggested to protect low-density lipoprotein (LDL) particles from oxidation. Hence, the antioxidant function of the redox couple RRR-alpha-TQ/RRR-alpha-TQH(2) in blocking LDL oxidation may reduce cellular cholesterol uptake and thus explain how SPF upregulates cholesterol synthesis.
- Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, University of Berne, 3012 Bern, Switzerland. achim.stocker@ibc.unibe.ch
Organizational Affiliation: