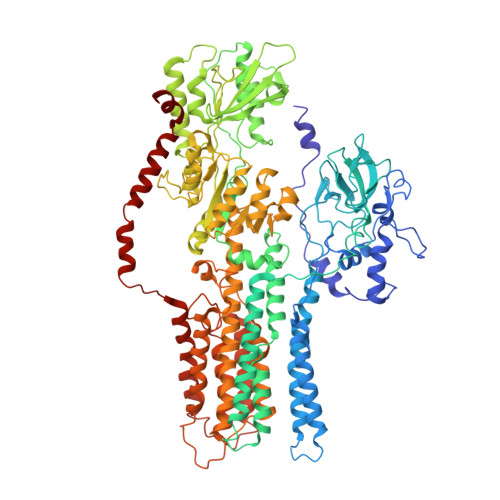
Structure, mechanism and regulation of the Neurospora plasma membrane H+-ATPase
Kuhlbrandt, W., Zeelen, J., Dietrich, J.(2002) Science 297: 1692-1696
- PubMed: 12169656
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1072574
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1MHS - PubMed Abstract:
Proton pumps in the plasma membrane of plants and yeasts maintain the intracellular pH and membrane potential. To gain insight into the molecular mechanisms of proton pumping, we built an atomic homology model of the proton pump based on the 2.6 angstrom x-ray structure of the related Ca2+ pump from rabbit sarcoplasmic reticulum. The model, when fitted to an 8 angstrom map of the Neurospora proton pump determined by electron microscopy, reveals the likely path of the proton through the membrane and shows that the nucleotide-binding domain rotates by approximately 70 degrees to deliver adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to the phosphorylation site. A synthetic peptide corresponding to the carboxyl-terminal regulatory domain stimulates ATPase activity, suggesting a mechanism for proton transport regulation.
- Max-Planck-Institut für Biophysik, Heinrich-Hoffmann-Str. 7, 60528 Frankfurt am Main, Germany.
Organizational Affiliation: