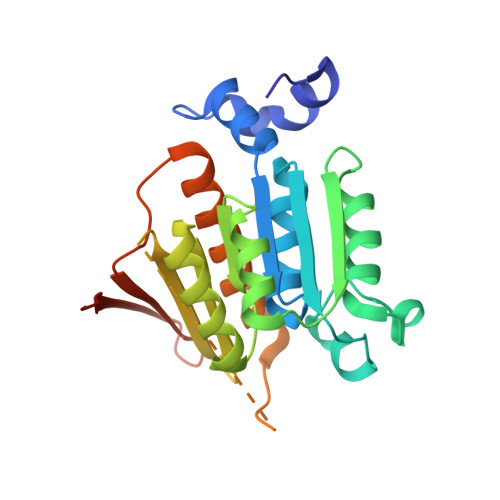
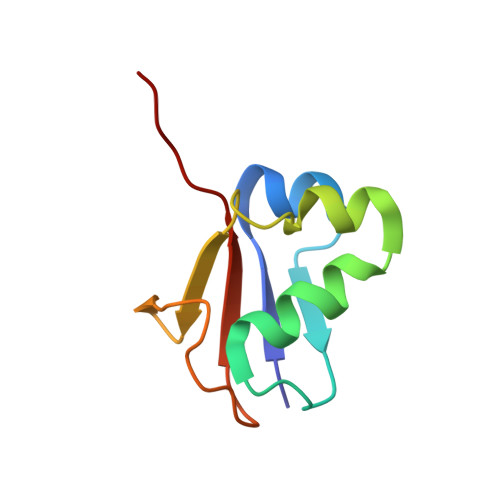
Mechanism of ubiquitin activation revealed by the structure of a bacterial MoeB-MoaD complex.
Lake, M.W., Wuebbens, M.M., Rajagopalan, K.V., Schindelin, H.(2001) Nature 414: 325-329
- PubMed: 11713534
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/35104586
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1JW9, 1JWA, 1JWB - PubMed Abstract:
The activation of ubiquitin and related protein modifiers is catalysed by members of the E1 enzyme family that use ATP for the covalent self-attachment of the modifiers to a conserved cysteine. The Escherichia coli proteins MoeB and MoaD are involved in molybdenum cofactor (Moco) biosynthesis, an evolutionarily conserved pathway. The MoeB- and E1-catalysed reactions are mechanistically similar, and despite a lack of sequence similarity, MoaD and ubiquitin display the same fold including a conserved carboxy-terminal Gly-Gly motif. Similar to the E1 enzymes, MoeB activates the C terminus of MoaD to form an acyl-adenylate. Subsequently, a sulphurtransferase converts the MoaD acyl-adenylate to a thiocarboxylate that acts as the sulphur donor during Moco biosynthesis. These findings suggest that ubiquitin and E1 are derived from two ancestral genes closely related to moaD and moeB. Here we present the crystal structures of the MoeB-MoaD complex in its apo, ATP-bound, and MoaD-adenylate forms, and highlight the functional similarities between the MoeB- and E1-substrate complexes. These structures provide a molecular framework for understanding the activation of ubiquitin, Rub, SUMO and the sulphur incorporation step during Moco and thiamine biosynthesis.
- Department of Biochemistry and Center for Structural Biology, State University of New York at Stony Brook, Stony Brook, New York 11794-5115, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: