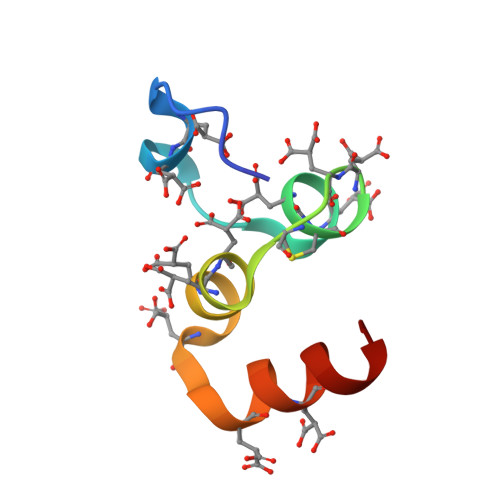
Crystal Structure of Mg2+- and Ca2+-bound Gla Domain of Factor IX Complexed with Binding Protein
Shikamoto, Y., Morita, T., Fujimoto, Z., Mizuno, H.(2003) J Biological Chem 278: 24090-24094
- PubMed: 12695512
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M300650200
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1J34, 1J35 - PubMed Abstract:
Factor IX is an indispensable protein required in the blood coagulation cascade. It binds to the surface of phospholipid membrane by means of a gamma-carboxyglutamic acid (Gla) domain situated at the N terminus. Recently, we showed that physiological concentrations of Mg2+ ions affect the native conformation of the Gla domain and in doing so augment the biological activity of factor IXa and binding affinity with its binding protein even in the presence of Ca2+ ions. Here we report on the crystal structures of the Mg2+/Ca2+-bound and Ca2+-bound (Mg2+-free) factor IX Gla domain (IXGD1-46) in complex with its binding protein (IX-bp) at 1.55 and 1.80 A resolutions, respectively. Three Mg2+ and five Ca2+ ions were bound in the Mg2+/Ca2+-bound IXGD1-46, and the Mg2+ ions were replaced by Ca2+ ions in Mg2+-free IXGD1-46. Comparison of Mg2+/Ca2+-bound with Ca2+-bound structures of the complexes showed that Mg2+ ion, which formed a bridge between IXGD1-46 and IX-bp, forced IXGD1-46 to rotate 4 degrees relative to IX-bp and hence might be the cause of a more tight interaction between the molecules than in the case of the Mg2+-free structure. The results clearly suggest that Mg2+ ions are required to maintain native conformation and in vivo function of factor IX Gla domain during blood coagulation.
- Department of Biochemistry, National Institute of Agrobiological Sciences, Kannondai 2-1-2, Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-8602, Japan.
Organizational Affiliation: