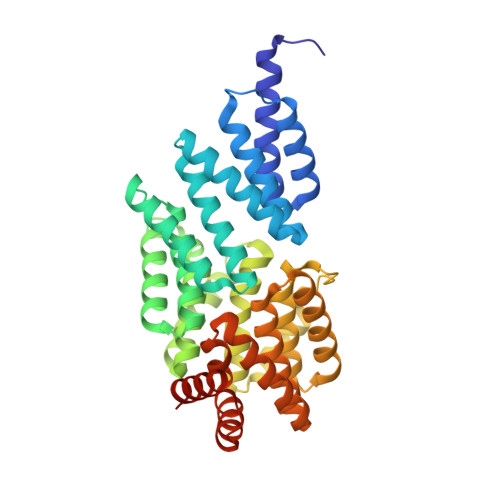
Crystal structure of transcription factor MalT domain III: a novel helix repeat fold implicated in regulated oligomerization.
Steegborn, C., Danot, O., Huber, R., Clausen, T.(2001) Structure 9: 1051-1060
- PubMed: 11709169
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0969-2126(01)00665-7
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1HZ4 - PubMed Abstract:
MalT from Escherichia coli, the best-studied member of the MalT family of ATP-dependent transcriptional activators, regulates the genes for malto-oligosaccharide utilization. The active form of this 4 domain protein is a homooligomer, and its multimerization is induced by the binding of maltotriose. Domains II and III of MalT were suggested to mediate the oligomerization process, but its molecular mechanism and the specific functions of these domains remain to be identified. We solved the crystal structure of MalT domain III at 1.45 A resolution by multiple isomorphous replacement phasing. The structure reveals eight copies of a two-helix bundle motif arranged in a novel, right-handed superhelix fold with closed walls, followed by a small C-terminal subdomain. The MalT superhelix contains a potential maltotriose binding site and forms a large hydrophobic protein-protein interaction interface that mediates the contact between two MalT domain III molecules. Structure-based analysis of the two-helix bundle motifs revealed a novel degenerated sequence pattern, and repeats of this pattern could be identified in other regulator proteins. MalT domain III contains a novel superhelix fold. Its protein-protein interaction interface, however, resembles protein binding sites of other superhelical proteins, suggesting a model with domain III mediating MalT oligomerization. Maltotriose seems to modulate the interaction interface and MalT oligomerization by occupying the ligand binding site inside the superhelix. Similar structural and mechanistic features in other MalT protein-family members and unrelated regulator proteins are indicated by the reappearance of a novel sequence motif derived from the MalT domain III structure.
- Max-Planck-Institut für Biochemie, Abteilung Strukturforschung, Am Klopferspitz 18a, 82152, Planegg-Martinsried, Germany. clemens_steegborn@gmx.de
Organizational Affiliation: