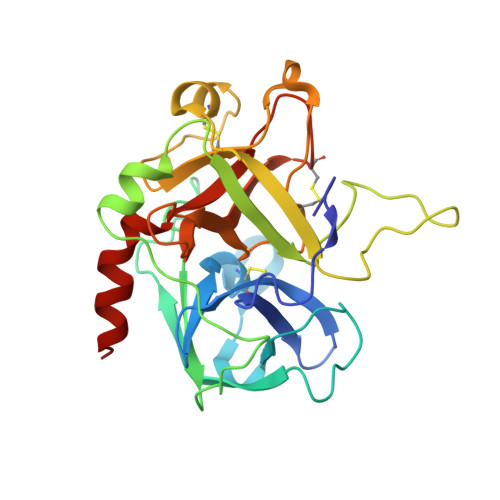
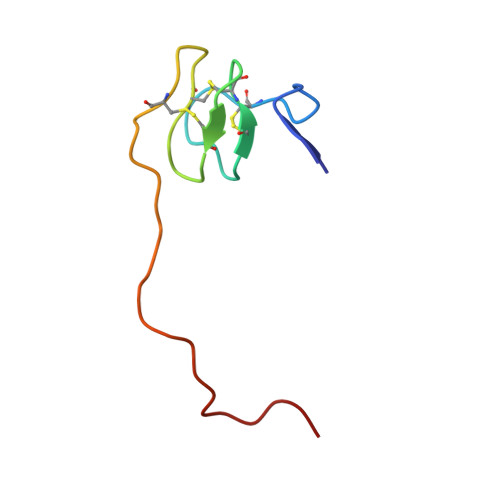
Crystal Structure of the Human Alpha-Thrombin-Haemadin Complex: An Exosite II-Binding Inhibitor
Richardson, J.L., Kroeger, B., Hoeffken, W., Sadler, J.E., Pereira, P., Huber, R., Bode, W., Fuentes-Prior, P.(2000) EMBO J 19: 5650
- PubMed: 11060016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/19.21.5650
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1E0F - PubMed Abstract:
The serine proteinase alpha-thrombin plays a pivotal role in the regulation of blood fluidity, and therefore constitutes a primary target in the treatment of various haemostatic disorders. Haemadin is a slow tight- binding thrombin inhibitor from the land-living leech Haemadipsa sylvestris. Here we present the 3.1 A crystal structure of the human alpha-thrombin- haemadin complex. The N-terminal segment of haemadin binds to the active site of thrombin, forming a parallel beta-strand with residues Ser214-Gly216 of the proteinase. This mode of binding is similar to that observed in another leech-derived inhibitor, hirudin. In contrast to hirudin, however, the markedly acidic C-terminal peptide of haemadin does not bind the fibrinogen-recognition exosite, but interacts with the heparin-binding exosite of thrombin. Thus, haemadin binds to thrombin according to a novel mechanism, despite an overall structural similarity with hirudin. Haemadin inhibits both free and thrombomodulin-bound alpha-thrombin, but not intermediate activation forms such as meizothrombin. This specific anticoagulant ability of haemadin makes it an ideal candidate for an antithrombotic agent, as well as a starting point for the design of novel antithrombotics.
- Max-Planck-Institut für Biochemie, D-82152 Martinsried, Department of Biotechnology, BASF Aktiengesellschaft, D-67056 Ludwigshafen, Germany. richards@biochem.mpg.de
Organizational Affiliation: