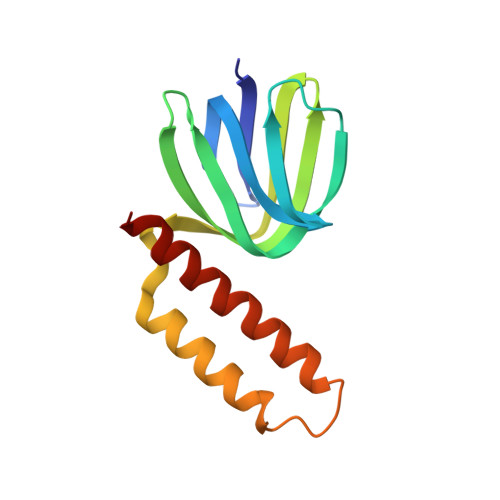
Crystal structure of the epsilon subunit of the proton-translocating ATP synthase from Escherichia coli.
Uhlin, U., Cox, G.B., Guss, J.M.(1997) Structure 5: 1219-1230
- PubMed: 9331422
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0969-2126(97)00272-4
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1AQT - PubMed Abstract:
Proton-translocating ATP synthases convert the energy generated from photosynthesis or respiration into ATP. These enzymes, termed F0F1-ATPases, are structurally highly conserved. In Escherichia coli, F0F1-ATPase consists of a membrane portion, F0, made up of three different polypeptides (a, b and c) and an F1 portion comprising five different polypeptides in the stoichiometry alpha 3 beta 3 gamma delta epsilon. The minor subunits gamma, delta and epsilon are required for the coupling of proton translocation with ATP synthesis; the epsilon subunit is in close contact with the alpha, beta, gamma and c subunits. The structure of the epsilon subunit provides clues to its essential role in this complex enzyme. The structure of the E. coli F0F1-ATPase epsilon subunit has been solved at 2.3 A resolution by multiple isomorphous replacement. The structure, comprising residues 2-136 of the polypeptide chain and 14 water molecules, refined to an R value of 0.214 (Rfree = 0.288). The molecule has a novel fold with two domains. The N-terminal domain is a beta sandwich with two five-stranded sheets. The C-terminal domain is formed from two alpha helices arranged in an antiparallel coiled-coil. A series of alanine residues from each helix form the central contacting residues in the helical domain and can be described as an 'alanine zipper'. There is an extensive hydrophobic contact region between the two domains providing a stable interface. The individual domains of the crystal structure closely resemble the structures determined in solution by NMR spectroscopy. Sequence alignments of a number of epsilon subunits from diverse sources suggest that the C-terminal domain, which is absent in some species, is not essential for function. In the crystal the N-terminal domains of two epsilon subunits make a close hydrophobic interaction across a crystallographic twofold axis. This region has previously been proposed as the contact surface between the epsilon and gamma subunits in the complete F1-ATPase complex. In the crystal structure we observe what is apparently a stable interface between the two domains of the epsilon subunit, consistent with the fact that the crystal and solution structures are quite similar despite close crystal packing. This suggests that a gross conformational change in the epsilon subunit, to transmit the effect of proton translocation to the catalytic domain, is unlikely, but cannot be ruled out.
- Department of Biochemistry, University of Sydney, NSW, Australia.
Organizational Affiliation: