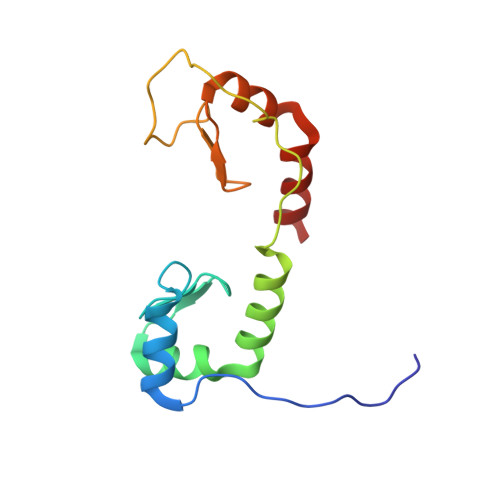
Solution structure of the N-terminal zinc fingers of the Xenopus laevis double-stranded RNA-binding protein ZFa
Moller, H.M., Martinez-Yamout, M.A., Dyson, H.J., Wright, P.E.(2005) J Mol Biology 351: 718-730
- PubMed: 16051273
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2005.06.032
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1ZU1 - PubMed Abstract:
Several zinc finger proteins have been discovered recently that bind specifically to double-stranded RNA. These include the mammalian JAZ and wig proteins, and the seven-zinc finger protein ZFa from Xenopus laevis. We have determined the solution structure of a 127 residue fragment of ZFa, which consists of two zinc finger domains connected by a linker that remains unstructured in the free protein in solution. The first zinc finger consists of a three-stranded beta-sheet and three helices, while the second finger contains only a two-stranded sheet and two helices. The common structures of the core regions of the two fingers are superimposable. Each finger has a highly electropositive surface that maps to a helix-kink-helix motif. There is no evidence for interactions between the two fingers, consistent with the length (24 residues) and unstructured nature of the intervening linker. Comparison with a number of other proteins shows similarities in the topology and arrangement of secondary structure elements with canonical DNA-binding zinc fingers, with protein interaction motifs such as FOG zinc fingers, and with other DNA-binding and RNA-binding proteins that do not contain zinc. However, in none of these cases does the alignment of these structures with the ZFa zinc fingers produce a consistent picture of a plausible RNA-binding interface. We conclude that the ZFa zinc fingers represent a new motif for the binding of double-stranded RNA.
- Department of Molecular Biology and Skaggs Institute for Chemical Biology, The Scripps Research Institute, 10550 North Torrey Pines Road, La Jolla, CA 92037, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: