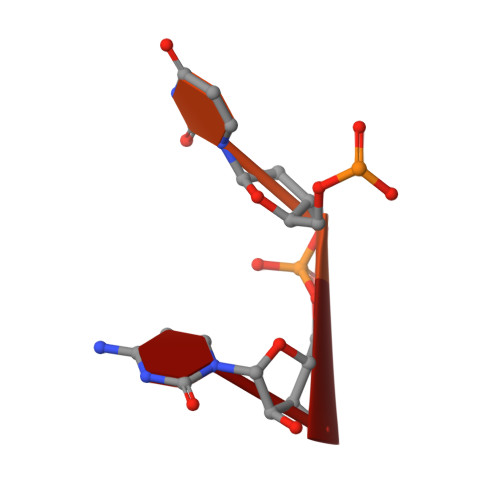
Structural mechanism of inhibition of the rho transcription termination factor by the antibiotic bicyclomycin
Skordalakes, E., Brogan, A.P., Park, B.S., Kohn, H., Berger, J.M.(2005) Structure 13: 99-109
- PubMed: 15642265
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2004.10.013
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1XPO, 1XPR, 1XPU - PubMed Abstract:
Rho is a hexameric RNA/DNA helicase/translocase that terminates transcription of select genes in bacteria. The naturally occurring antibiotic, bicyclomycin (BCM), acts as a noncompetitive inhibitor of ATP turnover to disrupt this process. We have determined three independent X-ray crystal structures of Rho complexed with BCM and two semisynthetic derivatives, 5a-(3-formylphenylsulfanyl)-dihydrobicyclomycin (FPDB) and 5a-formylbicyclomycin (FB) to 3.15, 3.05, and 3.15 A resolution, respectively. The structures show that BCM and its derivatives are nonnucleotide inhibitors that interact with Rho at a pocket adjacent to the ATP and RNA binding sites in the C-terminal half of the protein. BCM association prevents ATP turnover by an unexpected mechanism, occluding the binding of the nucleophilic water molecule required for ATP hydrolysis. Our data explain why only certain elements of BCM have been amenable to modification and serve as a template for the design of new inhibitors.
- Department of Molecular and Cell Biology, University of California, Berkeley, California 94720, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: