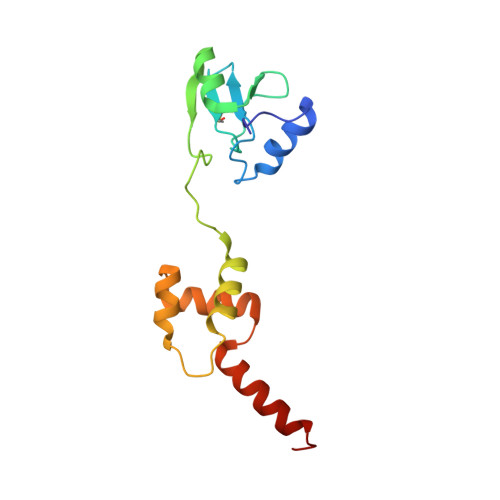
The solution structure of the methylated form of the N-terminal 16-kDa domain of Escherichia coli Ada protein
Takinowaki, H., Matsuda, Y., Yoshida, T., Kobayashi, Y., Ohkubo, T.(2006) Protein Sci 15: 487-497
- PubMed: 16452614
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1110/ps.051786306
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1WPK - PubMed Abstract:
The N-terminal 16-kDa domain of Escherichia coli Ada protein (N-Ada16k) repairs DNA methyl phosphotriester lesions by an irreversible methyl transfer to its cysteine residue. Upon the methylation, the sequence-specific DNA binding affinity for the promoter region of the alkylation resistance genes is enhanced by 10(3)-fold. Then, it acts as a transcriptional regulator for the methylation damage. In this paper, we identified the methyl acceptor residue of N-Ada16k and determined the solution structure of the methylated form of N-Ada16k by using NMR and mass spectrometry. The results of a 13C-filtered 1H-13C HMBC experiment and MALDI-TOF MS and MS/MS experiments clearly showed that the methyl acceptor residue is Cys38. The solution structure revealed that it has two distinct subdomains connected by a flexible linker loop: the methyltransferase (MTase) subdomain with the zinc-thiolate center, and the helical subdomain with a helix-turn-helix motif. Interestingly, there is no potential hydrogen bond donor around Cys38, whereas the other three cysteine residues coordinated to a zinc ion have potential donors. Hence, Cys38 could retain its inherent nucleophilicity and react with a methyl phosphotriester. Furthermore, the structure comparison shows that there is no indication of a remarkable conformational change occurring upon the methylation. This implies that the electrostatic repulsion between the negatively charged DNA and the zinc-thiolate center may avoid the contact between the MTase subdomain and the DNA in the nonmethylated form. Thus, after the Cys38 methylation, the MTase subdomain can bind the cognate DNA because the negative charge of the zinc-thiolate center is reduced.
- Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Osaka University, 1-6 Yamadaoka, Suita, Osaka 565-0871, Japan.
Organizational Affiliation: