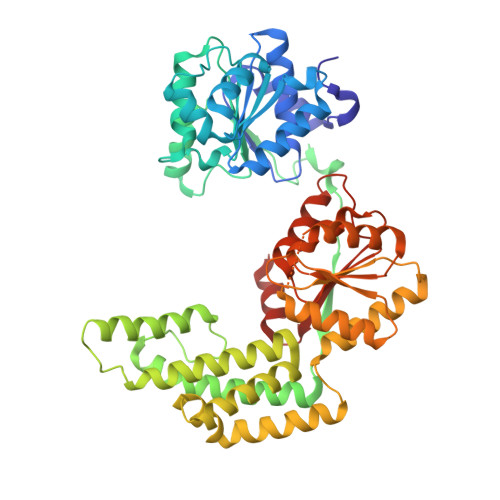
Crystal Structure and Functional Implications of Pyrococcus furiosus Hef Helicase Domain Involved in Branched DNA Processing
Nishino, T., Komori, K., Tsuchiya, D., Ishino, Y., Morikawa, K.(2005) Structure 13: 143-153
- PubMed: 15642269
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2004.11.008
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1WP9 - PubMed Abstract:
DNA and RNA frequently form various branched intermediates that are important for the transmission of genetic information. Helicases play pivotal roles in the processing of these transient intermediates during nucleic acid metabolism. The archaeal Hef helicase/ nuclease is a representative protein that processes flap- or fork-DNA structures, and, intriguingly, its C-terminal half belongs to the XPF/Mus81 nuclease family. Here, we report the crystal structure of the helicase domain of the Hef protein from Pyrococcus furiosus. The structure reveals a novel helical insertion between the two conserved helicase core domains. This positively charged extra region, structurally similar to the "thumb" domain of DNA polymerase, plays critical roles in fork recognition. The Hef helicase/nuclease exhibits sequence similarity to the Mph1 helicase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae; XPF/Rad1, involved in DNA repair; and a putative Hef homolog identified in mammals. Hence, our findings provide a structural basis for the functional mechanisms of this helicase/nuclease family.
- Department of Structural Biology, Biomolecular Engineering Research Institute, 6-2-3 Furuedai, Suita, Osaka 565-0874, Japan.
Organizational Affiliation: