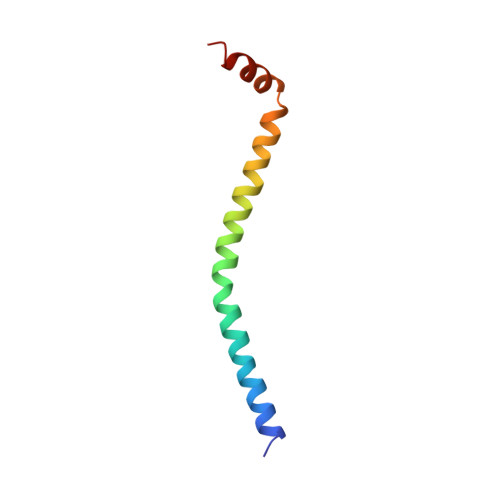
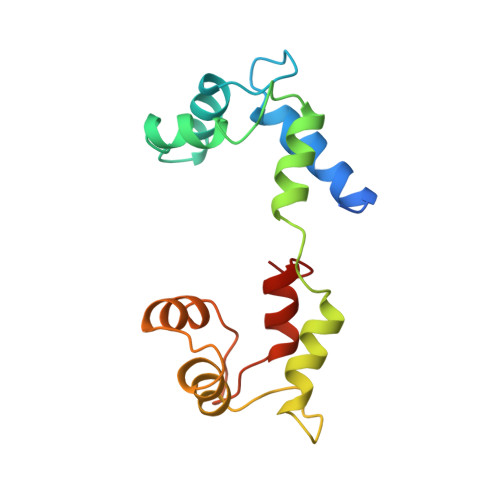
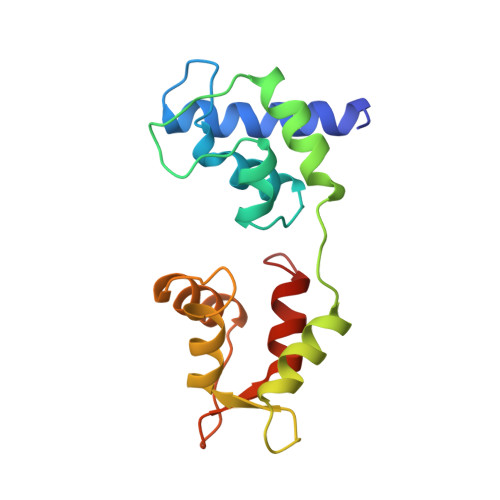
Structure of the regulatory domain of scallop myosin at 2 A resolution: implications for regulation.
Houdusse, A., Cohen, C.(1996) Structure 4: 21-32
- PubMed: 8805510
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0969-2126(96)00006-8
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1WDC - PubMed Abstract:
In contrast to the myosins of vertebrate skeletal muscle, molluscan myosins are regulated molecules whose enzymatic activity is switched on by the direct binding of Ca2+. The head portion (S1) of the molecule consists of a motor domain and a regulatory domain (RD) containing a 'regulatory' and an 'essential' light chain (RLC and ELC, respectively). The structures of scallop myosin RD with bound Ca2+, as well as the S1 fragment of chicken skeletal muscle myosin, have been determined previously to 2.8 A resolution. We have determined the structure at 2.0 A resolution of scallop myosin RD with bound Ca2+. The unusual coordination at the specific Ca(2+)-binding site in the ELC has now been clarified, as has the structural basis for Mg2+ binding to the RLC. A comparison of the scallop RD structure with that in the chicken S1 structure shows differences in the bending of the two RDs in two different places. Based on these structural results, a model for regulation is proposed in which the Ca(2+)-bound RD is a rigid structure, and transient flexibility of the Ca(2+)-free RD allows the myosin heads to make stabilizing intramolecular linkage which shut off the motor.
- Rosenstiel Basic Medical Sciences Research Center, Brandeis University, Waltham, MA 02254-9110, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: