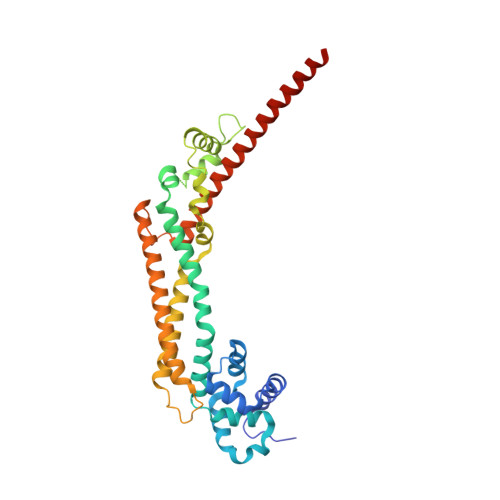
The core FH2 domain of diaphanous-related formins is an elongated actin binding protein that inhibits polymerization.
Shimada, A., Nyitrai, M., Vetter, I.R., Kuhlmann, D., Bugyi, B., Narumiya, S., Geeves, M.A., Wittinghofer, A.(2004) Mol Cell 13: 511-522
- PubMed: 14992721
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s1097-2765(04)00059-0
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1V9D - PubMed Abstract:
Diaphanous-related formins (Drf) are activated by Rho GTP binding proteins and induce polymerization of unbranched actin filaments. They contain three formin homology domains. Evidence as to the effect of formins on actin polymerization were obtained using FH2/FH1 constructs of various length from different Drfs. Here we define the core FH2 domain as a proteolytically stable domain of approximately 338 residues. The monomeric FH2 domains from mDia1 and mDia3 inhibit polymerization of actin and can bind in a 1:1 complex with F-actin at micromolar concentrations. The X-ray structure analysis of the domain shows an elongated, crescent-shaped molecule consisting of three helical subdomains. The most highly conserved regions of the domain span a distance of 75 A and are both required for barbed-end inhibition. A construct containing an additional 72 residue linker has dramatically different properties: It oligomerizes and induces actin polymerization at subnanomolar concentration.
- Max-Planck Institut für Molekulare Physiologie, Otto Hahn Strasse 11, D-44227 Dortmund, Germany.
Organizational Affiliation: