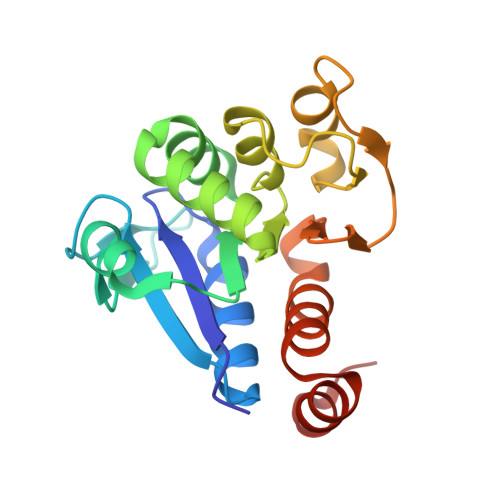
The Crystal Structure of DJ-1, a Protein Related to Male Fertility and Parkinson's Disease
Honbou, K., Suzuki, N.N., Horiuchi, M., Niki, T., Taira, T., Ariga, H., Inagaki, F.(2003) J Biological Chem 278: 31380-31384
- PubMed: 12796482
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M305878200
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1UCF - PubMed Abstract:
DJ-1 is a multifunctional protein that plays essential roles in tissues with higher order biological functions such as the testis and brain. DJ-1 is related to male fertility, and its level in sperm decreases in response to exposure to sperm toxicants. DJ-1 has also been identified as a hydroperoxide-responsive protein. Recently, a mutation of DJ-1 was found to be responsible for familial Parkinson's disease. Here, we present the crystal structure of DJ-1 refined to 1.95-A resolution. DJ-1 forms a dimer in the crystal, and the monomer takes a flavodoxin-like Rossmann-fold. DJ-1 is structurally most similar to the monomer subunit of protease I, the intracellular cysteine protease from Pyrococcus horikoshii, and belongs to the Class I glutamine amidotransferase-like superfamily. However, DJ-1 contains an additional alpha-helix at the C-terminal region, which blocks the putative catalytic site of DJ-1 and appears to regulate the enzymatic activity. DJ-1 may induce conformational changes to acquire catalytic activity in response to oxidative stress.
- Department of Structural Biology, Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Hokkaido University, N-12, W-6, Kita-ku, Sapporo, 060-0812, Japan.
Organizational Affiliation: