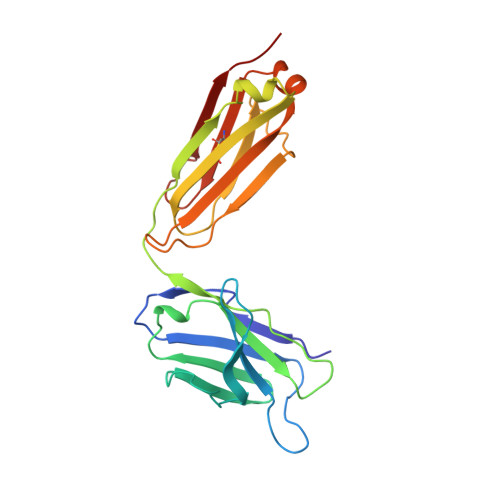
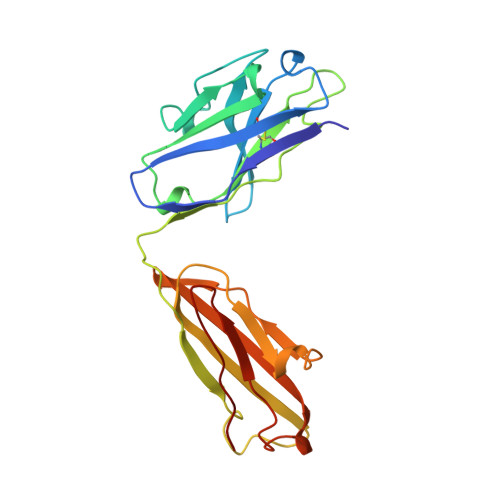
Structure of a monoclonal anti-ICAM-1 antibody R6.5 Fab fragment at 2.8 A resolution.
Jedrzejas, M.J., Miglietta, J., Griffin, J.A., Luo, M.(1995) Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 51: 380-385
- PubMed: 15299305
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S0907444994011054
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1RMF - PubMed Abstract:
The specific binding of the monoclonal murine anti-intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (anti-ICAM-1) antibody, R6.5, inhibits the attachment of neutrophils to endothelium and prevents the attachment of major group human rhinovirus (HRV) to ICAM-1. This binding interferes with the host immune system and, as a result, the R6.5 antibody has been developed as a therapeutic anti-inflammatory and perhaps anti-HRV agent. The variable-region amino-acid sequence of R6.5 was determined from the anti-ICAM-1 cDNA. The crystallization conditions of the Fab fragment of R6.5 were established and the three-dimensional structure was determined by X-ray crystallography. The crystal space group is orthorhombic P2(1)2(1)2(1), a = 40.36, b = 137.76, c = 91.32 A, and the highest resolution of recorded reflections is 2.7 A. The molecular-replacement method using known Fab structures was employed to solve the R6.5 Fab structure. The final R-factor is 18.8% for a total of 3320 non-H protein atoms, 39 water molecules and 10 606 unique reflections. The protein exhibits the typical immunoglobulin fold. The surface contour of the antigen-combining site of the R6.5 antibody has a wide groove which resembles more the structure of an anti-polypeptide antibody than the structure of an anti-protein antibody.
- Center for Macromolecular Crystallography, Department of Microbiology, University of Alabama at Birmingham, 35294, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: