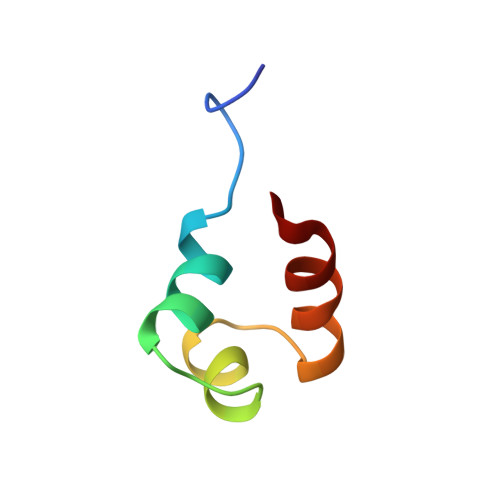
Determination of the structure of the DNA binding domain of gamma delta resolvase in solution.
Liu, T., DeRose, E.F., Mullen, G.P.(1994) Protein Sci 3: 1286-1295
- PubMed: 7987224
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/pro.5560030815
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1RES, 1RET - PubMed Abstract:
The DNA binding domain (DBD) of gamma delta resolvase (residues 141-183) is responsible for the interaction of this site-specific DNA recombinase with consensus site DNA within the gamma delta transposable element in Escherichia coli. Based on chemical-shift comparisons, the proteolytically isolated DBD displays side-chain interactions within a hydrophobic core that are highly similar to those of this domain when part of the intact enzyme (Liu T, Liu DJ, DeRose EF, Mullen GP, 1993, J Biol Chem 268:16309-16315). The structure of the DBD in solution has been determined using restraints obtained from 2-dimensional proton NMR data and is represented by 17 conformers. Experimental restraints included 458 distances based on analysis of nuclear Overhauser effect connectivities, 17 phi and chi 1 torsion angles based on analysis of couplings, and 17 backbone hydrogen bonds determined from NH exchange data. With respect to the computed average structure, these conformers display an RMS deviation of 0.67 A for the heavy backbone atoms and 1.49 A for all heavy atoms within residues 149-180. The DBD consists of 3 alpha-helices comprising residues D149-Q157, S162-T167, and R172-N183. Helix-2 and helix-3 form a backbone fold, which is similar to the canonical helix-turn-helix motif. The conformation of the NH2-terminal residues, G141-R148, appears flexible in solution. A hydrophobic core is formed by side chains donated by essentially all hydrophobic residues within the helices and turns. Helix-1 and helix-3 cross with a right-handed folding topology. The structure is consistent with a mechanism of DNA binding in which contacts are made by the hydrophilic face of helix-3 in the major groove and the amino-terminal arm in the minor groove. This structure represents an important step toward analysis of the mechanism of DNA interaction by gamma delta resolvase and provides initial structure-function comparisons among the divergent DBDs of related resolvases and invertases.
- Department of Chemistry, University of Wisconsin at Milwaukee 53211.
Organizational Affiliation: