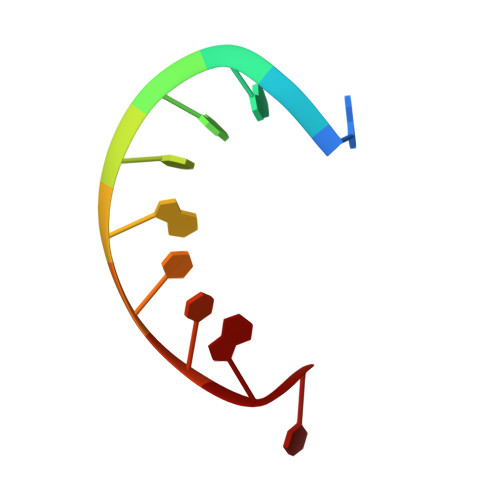
The structure of a chromosomal high mobility group protein-DNA complex reveals sequence-neutral mechanisms important for non-sequence-specific DNA recognition.
Murphy IV, F.V., Sweet, R.M., Churchill, M.E.(1999) EMBO J 18: 6610-6618
- PubMed: 10581235
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/18.23.6610
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1QRV - PubMed Abstract:
The high mobility group (HMG) chromosomal proteins, which are common to all eukaryotes, bind DNA in a non-sequence-specific fashion to promote chromatin function and gene regulation. They interact directly with nucleosomes and are believed to be modulators of chromatin structure. They are also important in V(D)J recombination and in activating a number of regulators of gene expression, including p53, Hox transcription factors and steroid hormone receptors, by increasing their affinity for DNA. The X-ray crystal structure, at 2.2 A resolution, of the HMG domain of the Drosophila melanogaster protein, HMG-D, bound to DNA provides the first detailed view of a chromosomal HMG domain interacting with linear DNA and reveals the molecular basis of non-sequence-specific DNA recognition. Ser10 forms water-mediated hydrogen bonds to DNA bases, and Val32 with Thr33 partially intercalates the DNA. These two 'sequence-neutral' mechanisms of DNA binding substitute for base-specific hydrogen bonds made by equivalent residues of the sequence-specific HMG domain protein, lymphoid enhancer factor-1. The use of multiple intercalations and water-mediated DNA contacts may prove to be generally important mechanisms by which chromosomal proteins bind to DNA in the minor groove.
- Department of Pharmacology, The University of Colorado Health Sciences Center, 4200 E. Ninth Avenue, Denver, CO 80262, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: