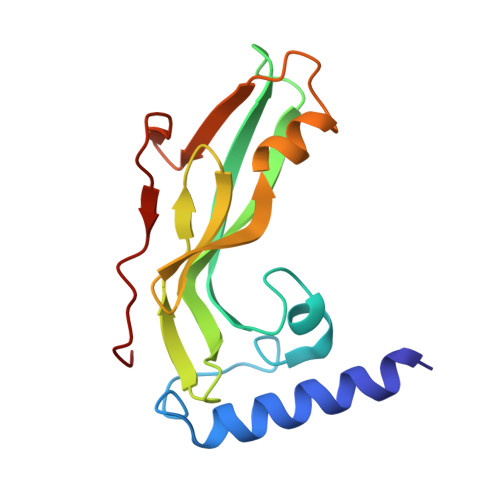
Crystal structure of the human papillomavirus type 18 E2 activation domain.
Harris, S.F., Botchan, M.R.(1999) Science 284: 1673-1677
- PubMed: 10356398
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.284.5420.1673
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1QQH - PubMed Abstract:
The papillomavirus E2 protein regulates viral transcription and DNA replication through interactions with cellular and viral proteins. The amino-terminal activation domain, which represents a protein class whose structural themes are poorly understood, contains key residues that mediate these functional contacts. The crystal structure of a protease-resistant core of the human papillomavirus type 18 E2 activation domain reveals a novel fold creating a cashew-shaped form with a glutamine-rich alpha helix packed against a beta-sheet framework. The protein surface shows extensive overlap of determinants for replication and transcription. The structure broadens the concept of activators to include proteins with potentially malleable, but certainly ordered, structures.
- Department of Molecular and Cell Biology, University of California, Berkeley, CA 94720-3204, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: