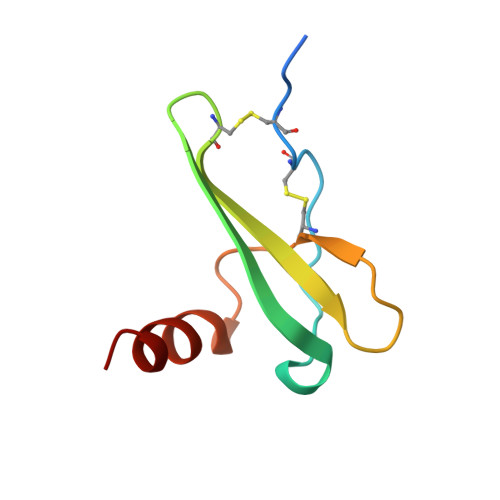
Crystal structure of recombinant native SDF-1alpha with additional mutagenesis studies: an attempt at a more comprehensive interpretation of accumulated structure-activity relationship data.
Ohnishi, Y., Senda, T., Nandhagopal, N., Sugimoto, K., Shioda, T., Nagal, Y., Mitsui, Y.(2000) J Interferon Cytokine Res 20: 691-700
- PubMed: 10954912
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1089/10799900050116390
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1QG7 - PubMed Abstract:
Crystal structures, forms 1 and 2, of recombinant native stromal cell-derived factor-1alpha (SDF-1alpha), expressed using the Sendai virus expression vector system, have been determined by x-ray crystallography at 2.0 A resolution. The crystal of form 1 is almost isomorphous with that used in the previous crystal structure analysis of the synthetic [N33A] mutant of SDF-1alpha (Dealwis, C., et al. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998;95, 6941-6946). However, the present structure analysis led to considerably better refinement statistics, revealing an error in the structural assignment of N-terminal residues in the previous report. Comparison of the solution structure, as previously determined by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, and the present structure, with two monomers in the asymmetric unit, reveals several local conformational differences. Alanine scan mutagenesis studies for each residue in the so-called RFFESH motif revealed that only the first residue, Arg12, is effective in enhancing receptor binding (and successive activation). A new notion that steric restraint between Arg8 and Arg12 is favorable (if not vital) for retaining SDF activities appears to explain more consistently the structure-activity relationship data accumulated to date. Four guiding principles are presented that may be useful for designing potent therapeutic compounds interfering with HIV-1 infection through competition at the CXCR4 coreceptor.
- Department of Viral Infection, Institute of Medical Science, University of Tokyo, Japan.
Organizational Affiliation: