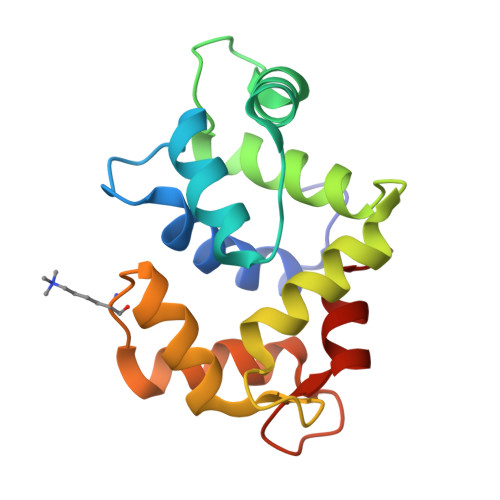
A closed compact structure of native ca(2+)-calmodulin.
Fallon, J.L., Quiocho, F.A.(2003) Structure 11: 1303-1307
- PubMed: 14527397
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2003.09.004
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1PRW - PubMed Abstract:
Calmodulin has been a subject of intense scrutiny since its discovery because of its unusual properties in regulating the functions of about 100 diverse target enzymes and structural proteins. The original and to date only crystal conformation of native eukaryotic Ca(2+)-calmodulin (Ca(2+)-CaM) is a very extended molecule with two widely separated globular domains linked by an exposed long helix. Here we report the 1.7 A X-ray structure of a new native Ca(2+)-CaM that is in a compact ellipsoidal conformation and shows a sharp bend in the linker helix and a more contracted N-terminal domain. This conformation may offer advantages for recognition of kinase-type calmodulin targets or small organic molecule drugs.
- Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX 77030, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: