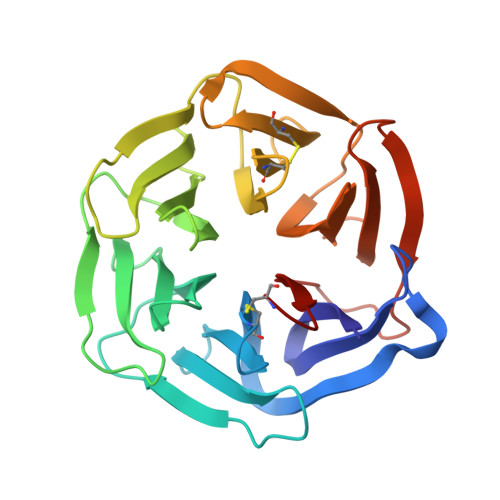
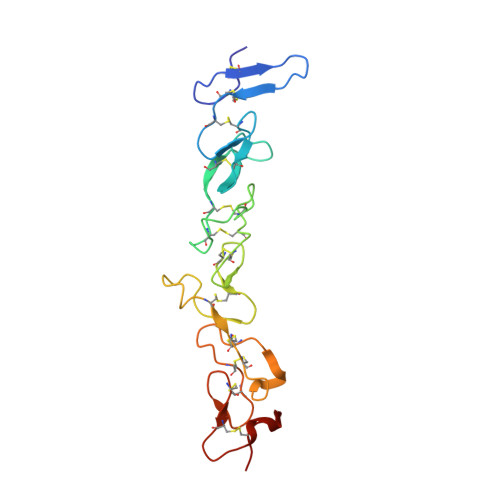
Complex between nidogen and laminin fragments reveals a paradigmatic beta-propeller interface
Takagi, J., Yang, Y.T., Liu, J.-H., Wang, J.-H., Springer, T.A.(2003) Nature 424: 969-974
- PubMed: 12931195
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01873
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1NPE - PubMed Abstract:
Basement membranes are fundamental to tissue organization and physiology in all metazoans. The interaction between laminin and nidogen is crucial to the assembly of basement membranes. The structure of the interacting domains reveals a six-bladed Tyr-Trp-Thr-Asp (YWTD) beta-propeller domain in nidogen bound to laminin epidermal-growth-factor-like (LE) modules III3-5 in laminin (LE3-5). Laminin LE module 4 binds to an amphitheatre-shaped surface on the pseudo-6-fold axis of the beta-propeller, and LE module 3 binds over its rim. A Phe residue that shutters the water-filled central aperture of the beta-propeller, the rigidity of the amphitheatre, and high shape complementarity enable the construction of an evolutionarily conserved binding surface for LE4 of unprecedentedly high affinity for its small size. Hypermorphic mutations in the Wnt co-receptor LRP5 (refs 6-9) suggest that a similar YWTD beta-propeller interface is used to bind ligands that function in developmental pathways. A related interface, but shifted off-centre from the pseudo-6-fold axis and lacking the shutter over the central aperture, is used in the low-density lipoprotein receptor for an intramolecular interaction that is regulated by pH in receptor recycling.
- The Center for Blood Research, Boston, Massachusetts 02115, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: