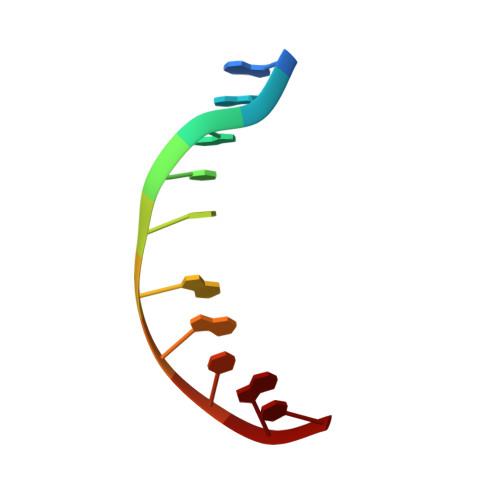
Structural refinement of the 8,9-dihydro-8-(N7-guanyl)-9-hydroxy-aflatoxin B(1) adduct in a 5'-Cp(AFB)G-3' sequence.
Giri, I., Jenkins, M.D., Schnetz-Boutaud, N.C., Stone, M.P.(2002) Chem Res Toxicol 15: 638-647
- PubMed: 12018984
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/tx010187n
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1MKL - PubMed Abstract:
The structure of the cationic 8,9-dihydro-8-(N7-guanyl)-9-hydroxy-aflatoxin B(1) adduct embedded in a 5'-CpG-3' sequence context and paired with deoxycytosine in the oligodeoxynucleotide d(ACATC(AFB)GATCT) x d(AGATCGATGT) was refined using molecular dynamics calculations restrained by NOE data and dihedral angle restraints obtained from NMR data. The aflatoxin moiety intercalated above the 5' face of the modified guanine. It stacked between C(5) x G(16) and (AFB)G(6) x C(15). The AFB(1) H5, OCH(3), and methylene protons faced into the minor groove, with the methylene protons oriented between the C(15) and G(16) nucleobases. The aflatoxin B(1) H6a, H8, H9, and H9a protons faced the major groove, with H6a and H9a pointing toward the 5' direction from the lesion site. The refined structure was compared to the structure of the aflatoxin B(1) adduct embedded in a 5'-ATGCAT-3' sequence in the oligodeoxynucleotide d(TAT(AFB)GCATA)(2) [Jones, W. R., Johnston, D. S., and Stone, M. P. (1998) Chem. Res. Toxicol.11, 873-881]. The structure of the intercalated aflatoxin B(1) lesion in the ATC(AFB)GAT sequence is similar to its structure in the d(AT(AFB)GCAT) sequence. This is consistent with a mechanism in which the precovalent intercalation of aflatoxin-8,9-exo-epoxide on the 5' face of guanine places the epoxide in close proximity and in the proper orientation to the N7 position of guanine, thus facilitating an S(N)2 reaction. The data provides additional insight into the nature of the disruption of the B-DNA duplex induced by aflatoxin B(1) intercalation. Overall, the results suggest that sequence contributes a minor role in modulating the structure of the cationic guanine N7 AFB(1) lesion in duplex DNA. On the other hand, structural differences are observed when the correctly paired structure is compared to the structure of the cationic AFB(1) adduct mispaired with dA [Giri, I., Johnston, D. S., and Stone, M. P. (2002) Biochemistry 41, 5462-5472].
- Department of Chemistry and Center in Molecular Toxicology, Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tennessee 37235, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: