The structure of human macrophage inflammatory protein-3alpha /CCL20. Linking antimicrobial and CC chemokine receptor-6-binding activities with human beta-defensins
Hoover, D.M., Boulegue, C., Yang, D., Oppenheim, J.J., Tucker, K., Lu, W., Lubkowski, J.(2002) J Biological Chem 277: 37647-37654
- PubMed: 12149255
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M203907200
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1M8A - PubMed Abstract:
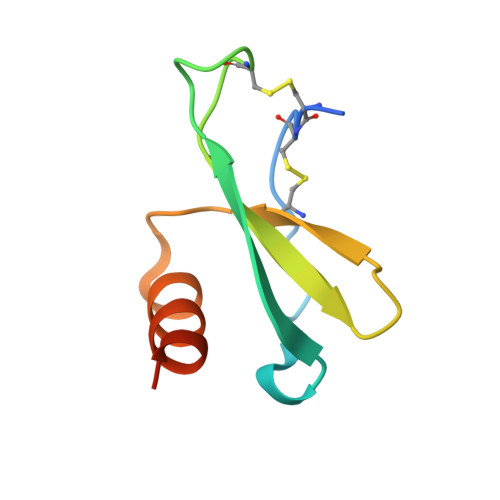
Human macrophage inflammatory protein-3alpha (MIP-3alpha; CCL20) is a CC-type chemokine that binds to and activates CC chemokine receptor-6 (CCR6). Although MIP-3alpha does not share the binding site of CCR6 with any other chemokine, human beta-defensin-1 and -2, small cationic antimicrobial peptides, have also been found to bind to and activate CCR6. Conversely, we have found that MIP-3alpha possesses antibacterial activity of greater potency than human beta-defensin-1 and -2 against Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 and Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29213, while having no activity against the fungus Candida albicans. There is no clear sequence similarity between beta-defensins and the chemokine MIP-3alpha, beyond an abundance of cationic residues and the presence of disulfide bonds. Nonetheless, there are structural similarities between these three proteins that allow their overlap of chemotactic and antimicrobial activities. In this report, we describe the x-ray crystal structure of human MIP-3alpha refined to a resolution of 1.7 A and compare it with the crystal structures of human beta-defensin-1 and -2. Molecules of MIP-3alpha and the beta-defensins seem to share few structural motifs that are likely associated with their common biological activities.
- Macromolecular Crystallography Laboratory, Division of Cancer Treatment, Centers and Diagnosis/Developmental Therapeutics Program, NCI-Frederick, Frederick, Maryland 21702, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: