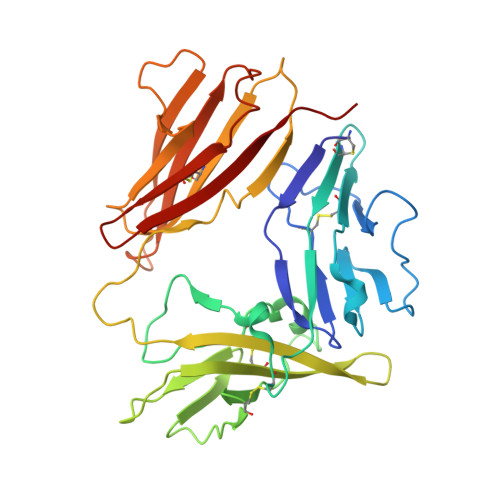
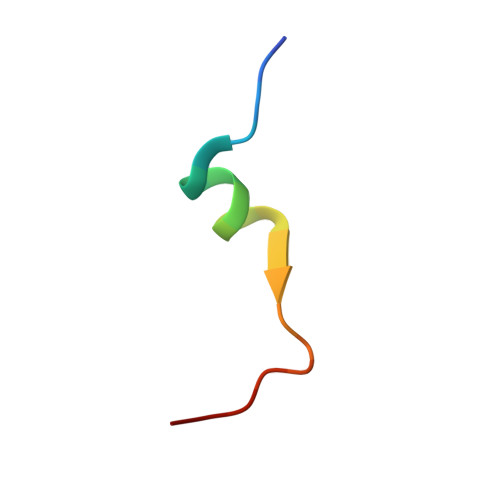
X-ray crystal structure of a small antagonist peptide bound to interleukin-1 receptor type 1.
Vigers, G.P., Dripps, D.J., Edwards III, C.K., Brandhuber, B.J.(2000) J Biological Chem 275: 36927-36933
- PubMed: 10903327
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M006071200
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1G0Y - PubMed Abstract:
Interleukin (IL-1)alpha and IL-1beta are important mediators of inflammation. The binding of IL-1 to interleukin-1 receptor (IL-1R) type 1 is the initial step in IL-1 signal transduction and therefore is a tempting target for anti-inflammatory therapeutics. To advance our understanding of IL-1R1 binding interactions, we have determined the structure of the extracellular domains of IL-1R1 bound to a 21-amino acid IL-1 antagonist peptide at 3.0-A resolution. The antagonist peptide binds to the domain 1/2 junction of the receptor, which is a conserved binding site for IL-1beta and IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1ra). This co-crystal structure also reveals that considerable flexibility is present in IL-1R1 because the carboxyl-terminal domain of the receptor is rotated almost 170 degrees relative to the first two domains of the receptor compared with the previously solved IL-1R1.ligand structures. The structure shows an unexpected binding mode for the peptide and may contribute to the design of smaller IL-1R antagonists.
- Department of Inflammation Research, Amgen, Incorporated, Boulder, Colorado 80301, USA. gvigers@arraybiopharma.com
Organizational Affiliation: