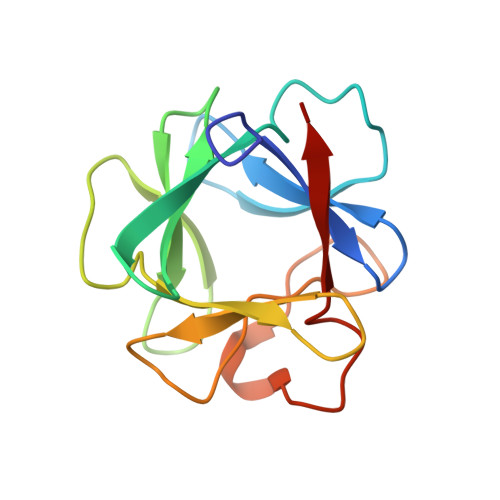
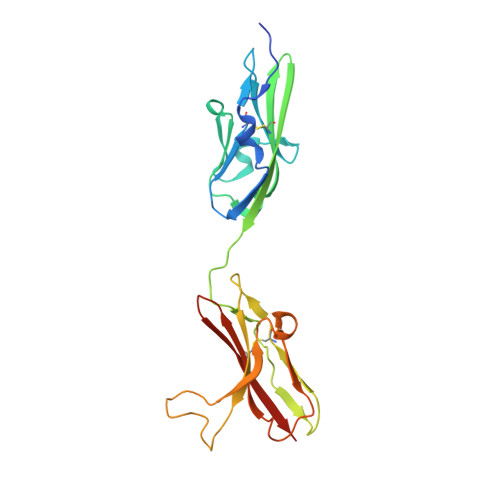
Crystal structure of a ternary FGF-FGFR-heparin complex reveals a dual role for heparin in FGFR binding and dimerization.
Schlessinger, J., Plotnikov, A.N., Ibrahimi, O.A., Eliseenkova, A.V., Yeh, B.K., Yayon, A., Linhardt, R.J., Mohammadi, M.(2000) Mol Cell 6: 743-750
- PubMed: 11030354
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s1097-2765(00)00073-3
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1FQ9 - PubMed Abstract:
The crystal structure of a dimeric 2:2:2 FGF:FGFR:heparin ternary complex at 3 A resolution has been determined. Within each 1:1 FGF:FGFR complex, heparin makes numerous contacts with both FGF and FGFR, thereby augmenting FGF-FGFR binding. Heparin also interacts with FGFR in the adjoining 1:1 FGF:FGFR complex to promote FGFR dimerization. The 6-O-sulfate group of heparin plays a pivotal role in mediating both interactions. The unexpected stoichiometry of heparin binding in the structure led us to propose a revised model for FGFR dimerization. Biochemical data in support of this model are also presented. This model provides a structural basis for FGFR activation by small molecule heparin analogs and may facilitate the design of heparin mimetics capable of modulating FGF signaling.
- Department of Pharmacology, New York University School of Medicine, New York, New York 10016, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: