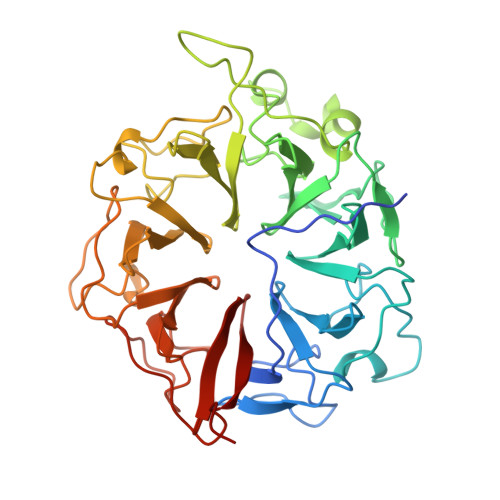
The 1.7 A crystal structure of the regulator of chromosome condensation (RCC1) reveals a seven-bladed propeller.
Renault, L., Nassar, N., Vetter, I., Becker, J., Klebe, C., Roth, M., Wittinghofer, A.(1998) Nature 392: 97-101
- PubMed: 9510255
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/32204
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1A12 - PubMed Abstract:
The gene encoding the regulator of chromosome condensation (RCC1) was cloned by virtue of its ability to complement the temperature-sensitive phenotype of the hamster cell line tsBN2, which undergoes premature chromosome condensation or arrest in the G1 phase of the cell cycle at non-permissive temperatures. RCC1 homologues have been identified in many eukaryotes, including budding and fission yeast. Mutations in the gene affect pre-messenger RNA processing and transport, mating, initiation of mitosis and chromatin decondensation, suggesting that RCC1 is important in the control of nucleo-cytoplasmic transport and the cell cycle. Biochemically, RCC1 is a guanine-nucleotide-exchange factor for the nuclear Ras homologue Ran; it increases the dissociation of Ran-bound GDP by 10(5)-fold. It may also bind to DNAvia a protein-protein complex. Here we show that the structure of human RCC1, solved to 1.7-A resolution by X-ray crystallography, consists of a seven-bladed propeller formed from internal repeats of 51-68 residues per blade. The sequence and structure of the repeats differ from those of WD40-domain proteins, which also form seven-bladed propellers and include the beta-subunits of G proteins. The nature of the structure explains the consequences of a wide range of known mutations. The region of the protein that is involved in guanine-nucleotide exchange is located opposite the region that is thought to be involved in chromosome binding.
- Abteilung Strukturelle Biologie, Max-Planck-Institut für Molekulare Physiologie, Dortmund, Germany.
Organizational Affiliation: