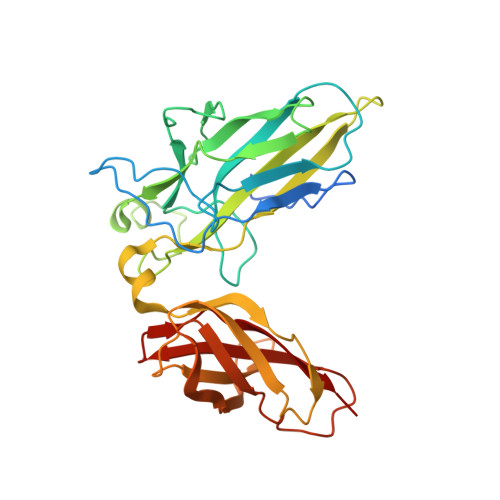
Structure of the DNA-binding domains from NFAT, Fos and Jun bound specifically to DNA.
Chen, L., Glover, J.N., Hogan, P.G., Rao, A., Harrison, S.C.(1998) Nature 392: 42-48
- PubMed: 9510247
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/32100
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1A02 - PubMed Abstract:
The nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFAT) and the AP-1 heterodimer, Fos-Jun, cooperatively bind a composite DNA site and synergistically activate the expression of many immune-response genes. A 2.7-A-resolution crystal structure of the DNA-binding domains of NFAT, Fos and Jun, in a quaternary complex with a DNA fragment containing the distal antigen-receptor response element from the interleukin-2 gene promoter, shows an extended interface between NFAT and AP-1, facilitated by the bending of Fos and DNA. The tight association of the three proteins on DNA creates a continuous groove for the recognition of 15 base pairs.
- Department of Molecular and Cellular Biology, Harvard University, Cambridge, Massachusetts 02138, USA. lchen@xta1200.harvard.edu
Organizational Affiliation: