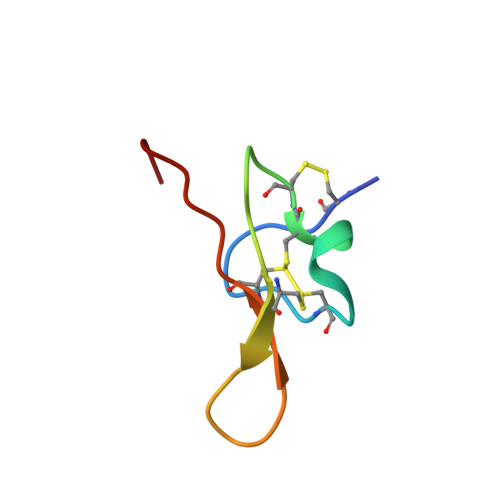
Structural and functional characterisation of Tst2, a novel TRPV1 inhibitory peptide from the Australian sea anemone Telmatactis stephensoni.
Elnahriry, K.A., Wai, D.C.C., Ashwood, L.M., Naseem, M.U., Szanto, T.G., Guo, S., Panyi, G., Prentis, P.J., Norton, R.S.(2023) Biochim Biophys Acta Proteins Proteom 1872: 140952
- PubMed: 37640250
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbapap.2023.140952
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8SEM - PubMed Abstract:
Sea anemone venoms are complex mixtures of biologically active compounds, including disulfide-rich peptides, some of which have found applications as research tools, and others as therapeutic leads. Our recent transcriptomic and proteomic studies of the Australian sea anemone Telmatactis stephensoni identified a transcript for a peptide designated Tst2. Tst2 is a 38-residue peptide showing sequence similarity to peptide toxins known to interact with a range of ion channels (Na V , TRPV1, K V and Ca V ). Recombinant Tst2 (rTst2, which contains an additional Gly at the N-terminus) was produced by periplasmic expression in Escherichia coli, enabling the production of both unlabelled and uniformly 13 C, 15 N-labelled peptide for functional assays and structural studies. The LC-MS profile of the recombinant Tst2 showed a pure peak with molecular mass 6 Da less than that of the reduced form of the peptide, indicating the successful formation of three disulfide bonds from its six cysteine residues. The solution structure of rTst2 was determined using multidimensional NMR spectroscopy and revealed that rTst2 adopts an inhibitor cystine knot (ICK) structure. rTst2 was screened using various functional assays, including patch-clamp electrophysiological and cytotoxicity assays. rTst2 was inactive against voltage-gated sodium channels (Na V ) and the human voltage-gated proton (hHv1) channel. rTst2 also did not possess cytotoxic activity when assessed against Drosophila melanogaster flies. However, the recombinant peptide at 100 nM showed >50% inhibition of the transient receptor potential subfamily V member 1 (TRPV1) and slight (∼10%) inhibition of transient receptor potential subfamily A member 1 (TRPA1). Tst2 is thus a novel ICK inhibitor of the TRPV1 channel.
- Medicinal Chemistry, Monash Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Monash University, Parkville, VIC 3052, Australia.
Organizational Affiliation: