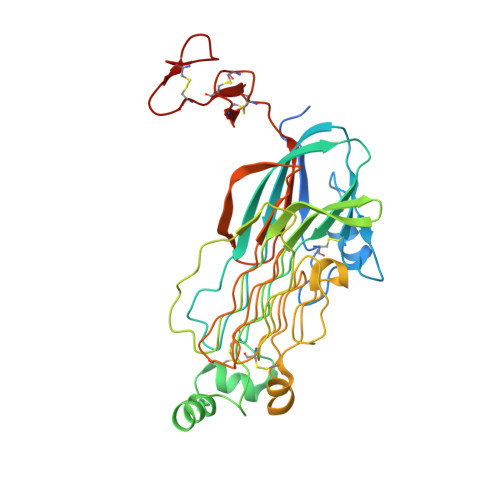
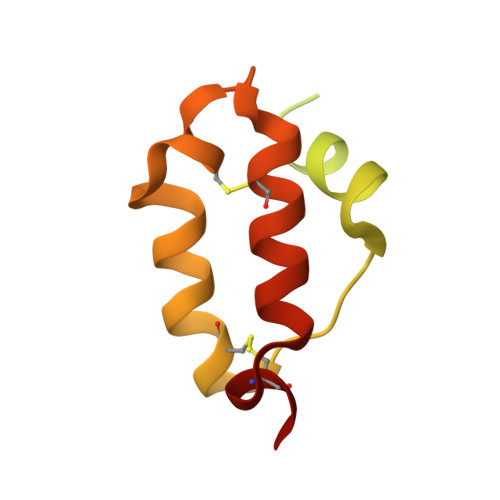
Mechanism for the activation of the anaplastic lymphoma kinase receptor.
Reshetnyak, A.V., Rossi, P., Myasnikov, A.G., Sowaileh, M., Mohanty, J., Nourse, A., Miller, D.J., Lax, I., Schlessinger, J., Kalodimos, C.G.(2021) Nature 600: 153-157
- PubMed: 34819673
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-04140-8
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7MZW, 7MZX, 7MZY, 7MZZ, 7N00 - PubMed Abstract:
Anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) is a receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) that regulates important functions in the central nervous system 1,2 . The ALK gene is a hotspot for chromosomal translocation events that result in several fusion proteins that cause a variety of human malignancies 3 . Somatic and germline gain-of-function mutations in ALK were identified in paediatric neuroblastoma 4-7 . ALK is composed of an extracellular region (ECR), a single transmembrane helix and an intracellular tyrosine kinase domain 8,9 . ALK is activated by the binding of ALKAL1 and ALKAL2 ligands 10-14 to its ECR, but the lack of structural information for the ALK-ECR or for ALKAL ligands has limited our understanding of ALK activation. Here we used cryo-electron microscopy, nuclear magnetic resonance and X-ray crystallography to determine the atomic details of human ALK dimerization and activation by ALKAL1 and ALKAL2. Our data reveal a mechanism of RTK activation that allows dimerization by either dimeric (ALKAL2) or monomeric (ALKAL1) ligands. This mechanism is underpinned by an unusual architecture of the receptor-ligand complex. The ALK-ECR undergoes a pronounced ligand-induced rearrangement and adopts an orientation parallel to the membrane surface. This orientation is further stabilized by an interaction between the ligand and the membrane. Our findings highlight the diversity in RTK oligomerization and activation mechanisms.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Structural Biology, St. Jude Children's Research Hospital, Memphis, TN, USA.