A Polyamide Inhibits Replication of Vesicular Stomatitis Virus by Targeting RNA in the Nucleocapsid.
Gumpper, R.H., Li, W., Castaneda, C.H., Scuderi, M.J., Bashkin, J.K., Luo, M.(2018) J Virol 92
- PubMed: 29437970
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.00146-18
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
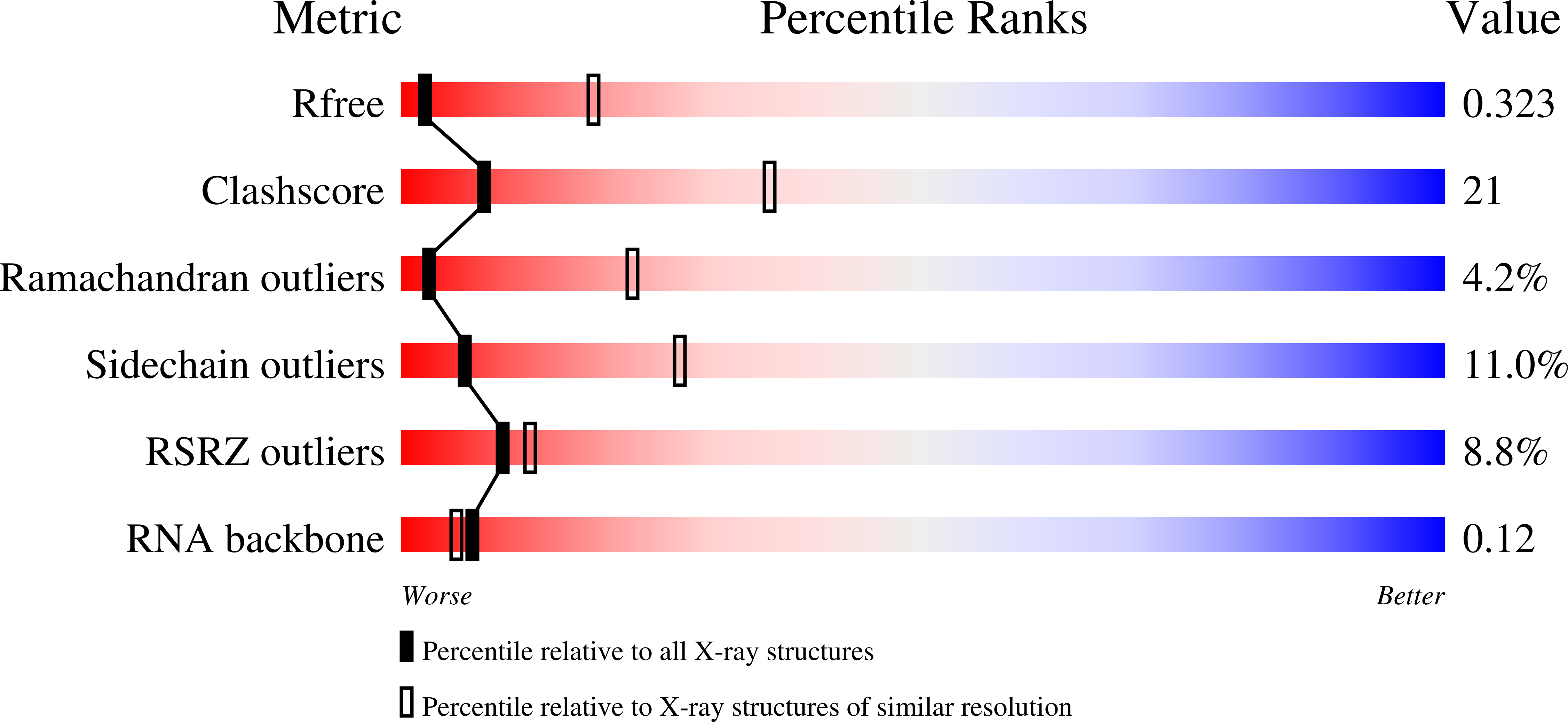
6BJY - PubMed Abstract:
Polyamides have been shown to bind double-stranded DNA by complementing the curvature of the minor groove and forming various hydrogen bonds with DNA. Several polyamide molecules have been found to have potent antiviral activities against papillomavirus, a double-stranded DNA virus. By analogy, we reason that polyamides may also interact with the structured RNA bound in the nucleocapsid of a negative-strand RNA virus. Vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) was selected as a prototype virus to test this possibility since its genomic RNA encapsidated in the nucleocapsid forms a structure resembling one strand of an A-form RNA duplex. One polyamide molecule, UMSL1011, was found to inhibit infection of VSV. To confirm that the polyamide targeted the nucleocapsid, a nucleocapsid-like particle (NLP) was incubated with UMSL1011. The encapsidated RNA in the polyamide-treated NLP was protected from thermo-release and digestion by RNase A. UMSL1011 also inhibits viral RNA synthesis in the intracellular activity assay for the viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. The crystal structure revealed that UMSL1011 binds the structured RNA in the nucleocapsid. The conclusion of our studies is that the RNA in the nucleocapsid is a viable antiviral target of polyamides. Since the RNA structure in the nucleocapsid is similar in all negative-strand RNA viruses, polyamides may be optimized to target the specific RNA genome of a negative-strand RNA virus, such as respiratory syncytial virus and Ebola virus. IMPORTANCE Negative-strand RNA viruses (NSVs) include several life-threatening pathogens, such as rabies virus, respiratory syncytial virus, and Ebola virus. There are no effective antiviral drugs against these viruses. Polyamides offer an exceptional opportunity because they may be optimized to target each NSV. Our studies on vesicular stomatitis virus, an NSV, demonstrated that a polyamide molecule could specifically target the viral RNA in the nucleocapsid and inhibit viral growth. The target specificity of the polyamide molecule was proved by its inhibition of thermo-release and RNA nuclease digestion of the RNA bound in a model nucleocapsid, and a crystal structure of the polyamide inside the nucleocapsid. This encouraging observation provided the proof-of-concept rationale for designing polyamides as antiviral drugs against NSVs.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry, Georgia State University, Atlanta, Georgia, USA.