An Atypical MAGUK GK Target Recognition Mode Revealed by the Interaction between DLG and KIF13B
Zhu, J., Shang, Y., Xia, Y., Zhang, R., Zhang, M.(2016) Structure 24: 1876-1885
- PubMed: 27642159
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2016.08.008
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
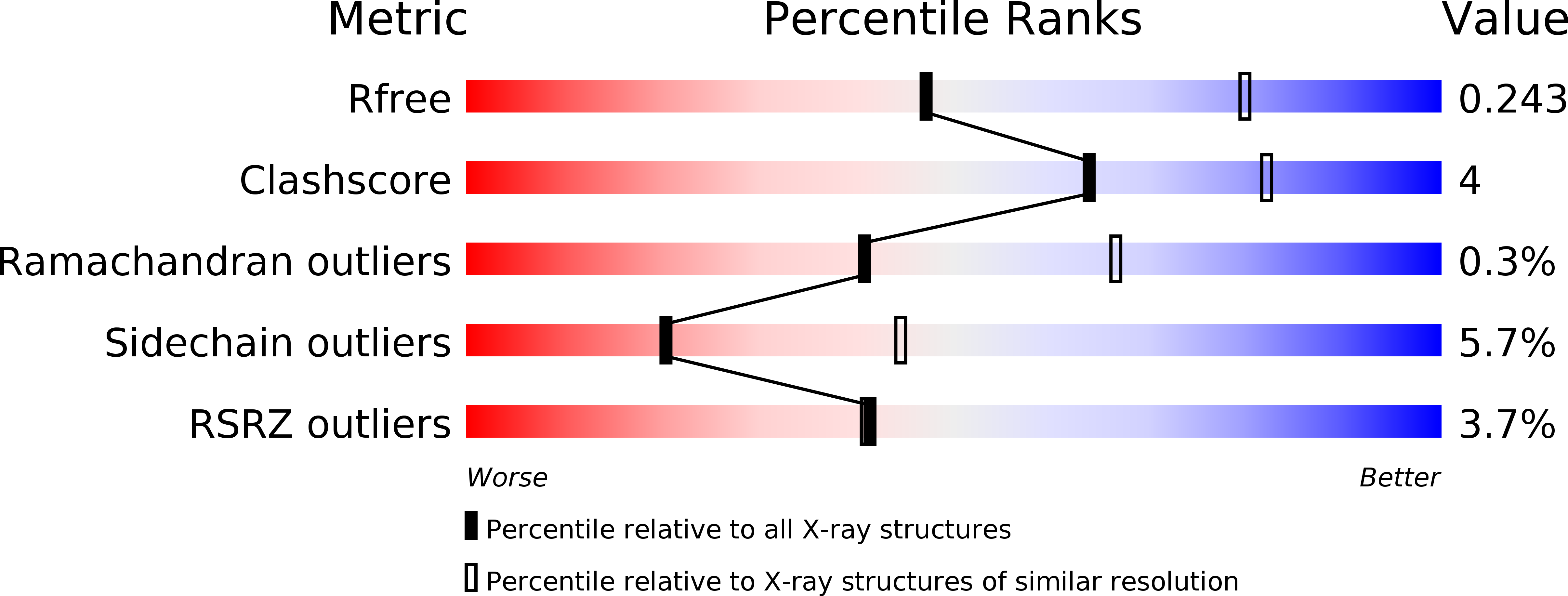
5B64 - PubMed Abstract:
The membrane-associated guanylate kinase (MAGUK) scaffold proteins share a signature guanylate kinase (GK) domain. Despite their diverse functional roles in cell polarity control and synaptic signaling, the currently known mode of action of MAGUK GK is via its binding to phosphorylated short peptides from target proteins. Here, we discover that the GK domain of DLG MAGUK binds to an unphosphorylated and autonomously folded domain within the stalk region (MAGUK binding stalk [MBS] domain) of a kinesin motor KIF13B with high specificity and affinity. The structure of DLG4 GK in complex with KIF13B MBS reveals the molecular mechanism governing this atypical GK/target recognition mode and provides insights into DLG/KIF13B complex-mediated regulation of diverse cellular processes such as asymmetric cell division. We further show that binding to non-phosphorylated targets is another general property of MAGUK GKs, thus expanding the mechanisms of action of the MAGUK family proteins.
Organizational Affiliation:
National Center for Protein Science Shanghai, Institute of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201210, China; Division of Life Science, State Key Laboratory of Molecular Neuroscience, Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, Clear Water Bay, Kowloon, Hong Kong, China. Electronic address: jinwei.zhu@sibcb.ac.cn.