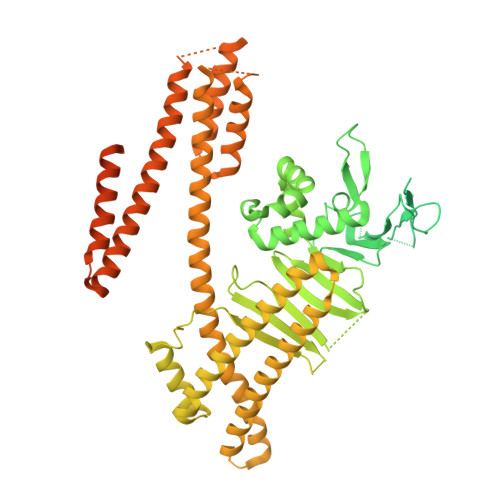
Structural insights into Helicobacter pylori oncoprotein CagA interaction with beta 1 integrin.
Kaplan-Turkoz, B., Jimenez-Soto, L.F., Dian, C., Ertl, C., Remaut, H., Louche, A., Tosi, T., Haas, R., Terradot, L.(2012) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109: 14640-14645
- PubMed: 22908298
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1206098109
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4G0H - PubMed Abstract:
Infection with the gastric pathogen Helicobacter pylori is a risk factor for the development of gastric cancer. Pathogenic strains of H. pylori carry a type IV secretion system (T4SS) responsible for the injection of the oncoprotein CagA into host cells. H. pylori and its cag-T4SS exploit α5β1 integrin as a receptor for CagA translocation. Injected CagA localizes to the inner leaflet of the host cell membrane, where it hijacks host cell signaling and induces cytoskeleton reorganization. Here we describe the crystal structure of the N-terminal ~100-kDa subdomain of CagA at 3.6 Å that unveils a unique combination of folds. The core domain of the protein consists of an extended single-layer β-sheet stabilized by two independent helical subdomains. The core is followed by a long helix that forms a four-helix helical bundle with the C-terminal domain. Mapping of conserved regions in a set of CagA sequences identified four conserved surface-exposed patches (CSP1-4), which represent putative hot-spots for protein-protein interactions. The proximal part of the single-layer β-sheet, covering CSP4, is involved in specific binding of CagA to the β1 integrin, as determined by yeast two-hybrid and in vivo competition assays in H. pylori cell-culture infection studies. These data provide a structural basis for the first step of CagA internalization into host cells and suggest that CagA uses a previously undescribed mechanism to bind β1 integrin to mediate its own translocation.
Organizational Affiliation:
Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique-Ligue Contre le Cancer, ATIP Avenir Group, Institut de Biologie et Chimie des Protéines, Unité Mixte de Recherche 5086, Université Lyon, Lyon F-69367, France.